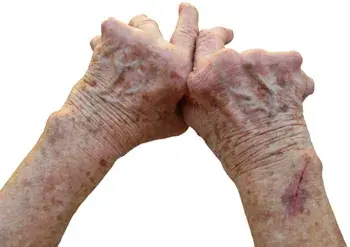
Rheumatoid arthritis is an auto immune disease primarily affecting the synovial tissues surrounding the joints. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), more than 1.5 million adults have this condition in the United States. As per recent reports, the number of people with arthritis is expected to reach 67 million by the end of 2030.
It is estimated that women suffer from this disease about two-and-a-half times more often than men do. This syndrome is very common in women between the age group of 30- 60 years and somewhat later in life in men. The life time risk of developing this disease is 4% in women whereas it is just 3% in men. However, scientists feel that hormones play a prominent role in this along with other factors such as genetics, lifestyle habits, age, sex and other environmental factors.
Children’s Genes May Increase Mothers’ Risk of Rheumatoid Arthritis
A new research paper presented at the American Society of Human Genetics (ASHG) 2014 Annual Meeting shows that children’s genes might increase their mothers’ risk for rheumatoid arthritis (RA). The new finding could possibly change the way physicians look at family history when advising women who are planning to conceive.
Researchers found a small number of fetal cells (known as fetal microchimerism) circulating around the mother’s body (during pregnancy) and some persisted for long as several decades. It was concluded those women who have this persistence of fetal cells have higher risk for developing this disease.
As part of the study, researchers analyzed the genes of mothers and children with and without the shared epitope or other forms of HLA genes associated with the risk of RA. The key findings include –
- Women having children with high-risk alleles (inherited from the father) increased their risk of developing this disease (even after checking for differences among the mothers’ genes).
- It was found that other than a woman’s own genetic risk of RA, there are several other additional risks conferred by carrying children with high-risk alleles.
Researchers have not been able to find the prominent reasons of how shared epitope and other HLA alleles influence RA risk. However, one possibility that they put forward is that the interactions between the proteins these genes encode may stimulate the autoimmune symptoms of the disease. A woman’s immune system may detect proteins produced by the fetus and incorrectly tag lingering fetal cells as a threat. This in turn may cause an immune reaction causing symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis.
How Do Physicians Diagnose Rheumatoid Arthritis?
There are different signs and symptoms associated with this disease and it may vary from one person to another. The intensity of the pain may be different from one person to another and will vary in severity. Some of the main symptoms include acute pain, joint swelling and inflammation, fatigue, joint stiffness and weight loss. In addition, RA also increases the potential risk of developing other diseases such as osteoporosis, carpel tunnel syndrome, stroke and cardiac problems.
Early diagnosis of the RA symptoms helps to effectively treat the disease and thereby prevent disability. However, it is very difficult to diagnose this disease in its early stages as the initial signs and symptoms are quite similar to that of many other diseases. There is no single blood test or other tests to verify the diagnosis. As part of the diagnosis, rheumatologists will check the joints for swelling, pain and muscle strength. They will perform a comprehensive diagnostic evaluation of the symptoms by conducting blood tests, X-rays etc. and clearly documenting them. Physicians have to utilize accurate diagnostic and procedural codes to report rheumatoid arthritis and its treatment. The following codes can be used –
- ICD-9-CM – 714.0 Rheumatoid arthritis
- ICD-10-CM – M06.9 Rheumatoid arthritis, unspecified
The treatment methodologies for this condition include medications, Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and physical therapy. Identifying the symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis at an early stage enables physicians to start treatment early. This in turn helps to reduce the debilitating effects of RA and improve the patient’s quality of life.