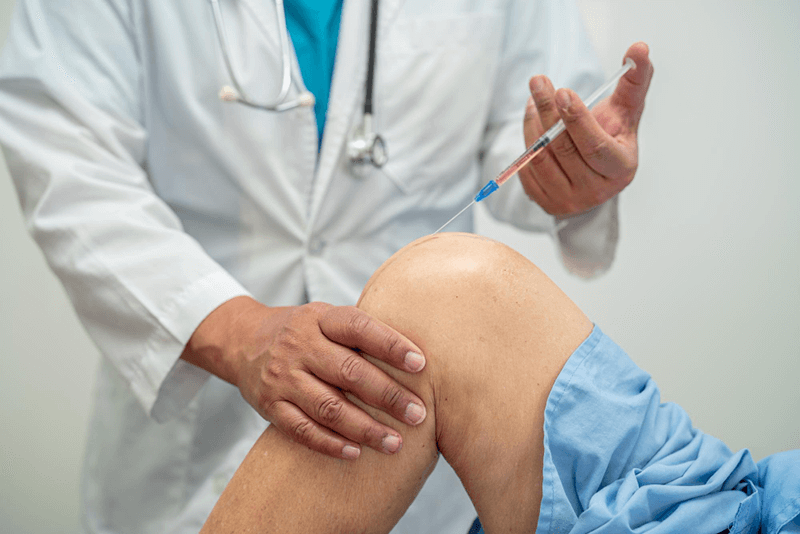
Certain medical conditions, injuries, and infections can cause joint effusion or build up of intraarticular fluid. Arthrocentesis involves performing joint aspiration/injections to establish a diagnosis, relieve discomfort, remove infected fluid, or inject medication. Coding for arthrocentesis can be complex. The physician should document a complete description of the procedure performed in the medical record. This will allow medical coding service providers to assign the proper codes to support the services rendered for appropriate reimbursement.
- Diagnostic and Therapeutic Joint Injections Medical conditions such as osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, gout, trauma, and Lyme disease can lead the joints to accumulate extra fluid. Arthrocentesis involves inserting a needle into a joint or bursa to inject medication, or aspirate fluid for diagnosis or pressure relief. Diagnostic joint injections are usually indicated when there is continual and unexplained pain, discomfort, and/or malfunction of a joint. Analysis of joint fluid can help determine the causes of joint swelling or effusion. To detect infection, the joint fluid is tested for various parameters such as white cell count, crystals, protein, and glucose, as well as cultured. Results can help physicians diagnose the type of arthritis, and also identify various potential rheumatology diseases and musculoskeletal conditions. Therapeutic joint injections for pain management are usually administered to treat inflammatory conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, gout, tendonitis, bursitis, and osteoarthritis. Corticosteroids, hyaluronic acid (HA), and anesthetics are among the injectables most commonly used to relieve patients’ symptoms. Joint aspirations/injections are performed under medical guidelines by general physicians, internists, orthopedic surgeons, rheumatologists, interventional radiologists, emergency room physicians, as well as nurse practitioners and physician assistants.
- Indications
Indications for diagnostic arthrocentesis include:- Evaluation of monoarticular arthritis, suspected septic arthritis, and joint effusion
- Identification of intra-articular fracture and crystal arthropathy
Indications for therapeutic arthrocentesis include:
- Pain relief of by aspirating effusion or hemarthrosis
- Instillation of medications
- Drainage of septic effusion
Joint aspiration is considered appropriate for any patient with an inflamed joint or joints who does not have an established diagnosis. Inflamed joints are recognized by being red, warm, tender, swollen, and painful to bend.
- Arthrocentesis CPT Codes
The CPT codes for arthrocentesis aspiration or injection procedures are 20600-20611. Accurate reimbursement depends on reporting the services provided using all the appropriate code sets and modifiers. Arthrocentesis CPT codes are categorized based on joint or bursa, and whether ultrasound guidance is performed:- 20600 Arthrocentesis, aspiration and/or injection, small joint or bursa (eg, fingers, toes); without ultrasound guidance
- 20604 Arthrocentesis, aspiration and/or injection, small joint or bursa (eg, fingers, toes); with ultrasound guidance, with permanent recording and reporting
- 20605 Arthrocentesis, aspiration and/or injection, intermediate joint or bursa (eg, temporomandibular, acromioclavicular, wrist, elbow or ankle, olecranon bursa); without ultrasound guidance
- 20606 Arthrocentesis, aspiration and/or injection, intermediate joint or bursa (eg, temporomandibular, acromioclavicular, wrist, elbow or ankle, olecranon bursa); with ultrasound guidance, with permanent recording and reporting
- 20610 Arthrocentesis, aspiration and/or injection, major joint or bursa (eg, shoulder, hip, knee, subacromial bursa); without ultrasound guidance
- 20611 Arthrocentesis, aspiration and/or injection, major joint or bursa (eg, shoulder, hip, knee, subacromial bursa); with ultrasound guidance, with permanent recording and reporting
- Considerations when Using Joint Aspiration/Injection Codes
CPT codes for joint aspiration/injection are categorized on the basis of the type of joint or bursa and other considerations. Here are the important points to note while selecting a code:- Type of joint or bursa and if ultrasound was performed: In 2015, joint (or bursa) aspiration/injection codes were revised to indicate “without ultrasonic guidance,” and codes were added describe the same procedures with ultrasonic (US) guidance. Codes 20604, 20606, or 20611 should be used if joint aspiration/injection was performed with ultrasound guidance. Codes 20600, 20605, and 20610 apply if aspiration/injection of the joint/bursa was performed without guidance of any kind.
A November 2017 AAPC article provides guidance on using these CPT codes based on the targeted joints or bursa and whether ultrasound is performed:- CPT codes 20600 or 20604 for small joints or bursa
20600 Arthrocentesis, aspiration and/or injection, small joint or bursa (eg, fingers, toes); without ultrasound guidance, or
20604 Arthrocentesis, aspiration and/or injection, small joint or bursa (eg, fingers, toes); with ultrasound guidance, with permanent recording and reporting. - CPT codes 20605 or 20606 for intermediate joints or bursa
20605 Arthrocentesis, aspiration and/or injection, intermediate joint or bursa (eg, temporomandibular, acromioclavicular, wrist, elbow or ankle, olecranon bursa); without ultrasound guidance, or
20606 Arthrocentesis, aspiration and/or injection, intermediate joint or bursa (eg, temporomandibular, acromioclavicular, wrist, elbow or ankle, olecranon bursa); with ultrasound guidance, with permanent recording and reporting. - 20610 or 20611 for major joints or bursa
20610 Arthrocentesis, aspiration and/or injection, major joint or bursa (eg, shoulder, hip, knee, subacromial bursa); without ultrasound guidance, or
20611 Arthrocentesis, aspiration and/or injection, major joint or bursa (eg, shoulder, hip, knee, subacromial bursa); with ultrasound guidance, with permanent recording and reporting.
- CPT codes 20600 or 20604 for small joints or bursa
- Type of joint or bursa and if ultrasound was performed: In 2015, joint (or bursa) aspiration/injection codes were revised to indicate “without ultrasonic guidance,” and codes were added describe the same procedures with ultrasonic (US) guidance. Codes 20604, 20606, or 20611 should be used if joint aspiration/injection was performed with ultrasound guidance. Codes 20600, 20605, and 20610 apply if aspiration/injection of the joint/bursa was performed without guidance of any kind.
- When to report a radiology code: if fluoroscopic, computed tomography (CT), or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) guidance is performed, the following radiology codes should also be reported:
- +77002 Fluoroscopic guidance for needle placement (eg, biopsy, aspiration, injection, localization device) (List separately in addition to code for primary procedure)
- 77012 Computed tomography guidance for needle placement (eg, biopsy, aspiration, injection, localization device), radiological supervision and interpretation
- 77021 Magnetic resonance guidance for needle placement (eg, for biopsy, needle aspiration, injection, or placement of localization device) radiological supervision and interpretation
- Distinct codes to report cysts: There are separate codes for aspiration and/or injection into a ganglion cyst or for treatment of a bone cyst:
- 20612 Aspiration and/or injection of ganglion cyst(s) any location
For multiple ganglion cysts, modifier 59 Distinct procedural service should be appended when reporting 20612 - 20615 Aspiration and injection for treatment of bone cyst
- 20612 Aspiration and/or injection of ganglion cyst(s) any location
- Joint Aspiration/Injection Coding – Important Billing Points
- CPT recommends reporting a single unit of 20600-20611 for each joint treated, regardless of how many aspirations and/or injections occur in a single joint.
- If the procedure is performed on multiple joints, separate codes should be reported for each joint.
- Multiple units of a single code can be reported for aspiration/injection of multiple joints of same size (e.g., two large joints, left knee and left shoulder).
- According to Centers for Medicare & Medicaid (CMS) guidelines, one unit of 20610 should be reported with modifier 50 Bilateral procedure appended if aspirations and/or injections occur on opposite, paired joints (e.g., both knees). Non-Medicare payers may have different rules for reporting a bilateral procedure.
- If injections are performed on separate, non-symmetrical joints (e.g., left shoulder and right knee), two units of the aspiration/injection code should be reported and modifier 59 Distinct procedural service should be appended to the second unit (e.g., 20610, 20610-59).
- If medication is injected, the appropriate HCPCS Level II J code should be reported.
- An evaluation and management (E/M) service can be reported with the arthrocentesis, aspiration, or injection codes, provided the service is significant and separately identifiable from the procedure. Modifier 25 Significant, separately identifiable evaluation and management service by the same physician or other qualified health care professional on the same day of the procedure or other service should be appended to the appropriate E/M service code.
- A separate E/M service should not be reported if the patient reports to the office strictly for the aspiration, arthrocentesis, or injection procedure.
- Modifier LT Left side or modifier RT Right side may be appropriate when reporting codes for joint arthrocentesis, aspiration, or injection procedures. For instance, AAPC says that if a patient presents to the office for an injection of 40 mg of triamcinolone to the left hip for trochanteric bursitis of the left hip, it should be reported as follows:
- 20610-LT
- J3301 Injection, triamcinolone acetonide, not otherwise specified, 10 mg x 4
- M70.62 Trochanteric bursitis, left hip
Outsourcing medical billing and coding to a company with extensive expertise in reporting arthrocentesis, joint aspiration and injection is a viable option. Experienced companies have AAPC-certified coders who are well-versed in reporting these procedures and also knowledgeable about the coverage policies of Medicare, Medicaid, and commercial payers. They can ensure that claims are submitted with the appropriate CPT codes and diagnosis codes to support the medical necessity of the procedures performed and ordered.
Optimize your coding operations with our professional medical coding service!
Talk to our team at (800) 670-2809!