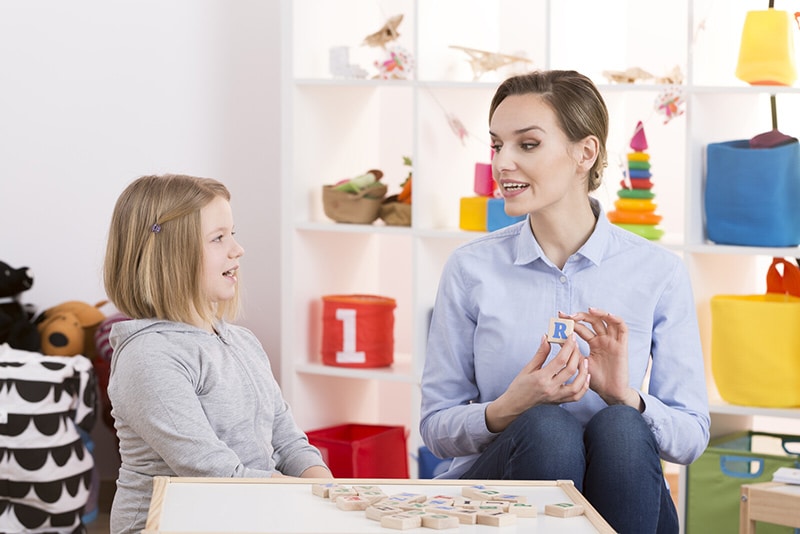
Early intervention provides infants and toddlers with development delays the support they need to make progress and reach their developmental milestones. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) defines early intervention as “the services and supports that are available to babies and young children with developmental delays and disabilities and their families”. The services may include speech therapy, physical therapy, and other types of services to meet the needs of the child and family. Early intervention can take various forms and be provided in various settings. Audiologists and speech-language pathologists can outsource medical billing and coding to report these services successfully on claims.
Early intervention basically aims to develop a child’s skills in five areas:
- Cognitive development
- Communication development
- Sensory development, including vision and hearing
- Social or emotional development
- Adaptive development
These services have a significant impact on infants and toddlers at risk for a disability or development delays by improving their ability to learn new skills, overcome challenges and helping them succeed in school and life.
Eligibility is determined by evaluating the infant/toddler to see if the child does have a delay in development or a disability. For some children, early intervention will be needed from birth through the third birthday, and sometimes, even after this. Other children need early intervention because they develop more slowly than children of their age should, experience setbacks, or develop in ways that appears very different from other children. Early intervention programs are available in every state and territory, but services provided may vary. Clinicians need to contact the payer or program for queries/consultations on coding or coverage.
Coding for Early Intervention
EI services may include the following:
- Audiologic services
- Assistive technology
- Counseling/psychological services
- Family training, counseling and home visits
- Medical evaluation (for diagnostic purposes only)
- Nursing services
- Nutritional services
- Occupational therapy
- Physical therapy
- Service coordination
- Social work services
- Special instruction
- Speech/language therapy
- Sign language and cued speech services
- Vision services
- Transportation
Coding for early intervention depends on what the services are, where they are provided, and other factors, according to an American Speech-Language-Hearing Association (ASHA) article.
Place of Service (POS): Services may be provided in the home, office, daycare, school, or other specialized program setting. The setting must be reported on the claim using the correct two-digit POS code. Examples of POS codes include:
03 School
11 Office and
12 Home
As there is variability across EI programs on reporting POS codes, ASHA recommends that providers should directly consult the EI program or payer on the code to use, especially if services are provided outside the conventional office or clinic setting.
Evaluation and Treatment: There are several CPT, ICD-10 and HCPCS codes to report audiology and speech-language pathology services. HCPCS Level II codes are used to report devices and durable medical equipment (such as hearing aids or speech-generating devices) as well as some other services.
CPT Codes for Audiologic Testing: Chances of developmental delay are higher in children who are born deaf or hard of hearing (D/HH) as they may lack early exposure to an accessible language. Such children may also have other conditions at birth that can result in developmental delays. Early intervention, when provided as soon as possible, will ensure that D/HH children can reach their full potential. Early Intervention represents the goal of the entire Early Hearing Detection and Intervention (EHDI) process. Commonly used audiologic testing CPT codes include:
- 92550–92587 – comprehensive audiometry, acoustic immittance, and auditory evoked potentials testing
Codes for hearing implant-related evaluations:
- 92626 Evaluation of auditory function for surgically implanted device(s) candidacy or postoperative status of a surgically implanted device(s); first hour
- 92627 Evaluation of auditory function for surgically implanted device(s) candidacy or postoperative status of a surgically implanted device(s); each additional 15 minutes (List separately in addition to code for primary procedure)
General guidelines:
- Choose the CPT code that best represents the testing technique used.
- Most audiology CPT codes (other than VRA) are valued based on the procedure being performed on both ears. If testing is done on only one ear, reduced service modifier -52 may be appended to indicate that the entire procedure was not completed.
- Append appropriate modifiers when billing services on a claim. The TL modifier should be placed in the first position on the claim for Early Intervention Services therapy.
- The medical record documentation should support the reason that testing was completed and the reasons for billing specific codes. Missing or incomplete documentation can lead to claim denial.
- When using time-based codes, the audiologist has to properly list evaluation start and end times in the patient’s medical record.
Speech Therapy and Early Intervention Programs – CPT and HCPCS Codes
CPT codes for speech and language evaluations include:
92507 Treatment of speech, language, voice, communication, and/or auditory processing disorder; individual
92508 Treatment of speech, language, voice, communication, and/or auditory processing disorder; group, 2 or more individuals
92521 Evaluation of speech fluency (e.g., stuttering, cluttering)
92522 Evaluation of speech sound production (e.g., articulation, phonological process, apraxia, dysarthria);
92523 Evaluation of speech sound production (e.g., articulation, phonological process, apraxia, dysarthria); with evaluation of language comprehension and expression (e.g., receptive and expressive language)
92524 Behavioral and qualitative analysis of voice and resonance
92526 Treatment of swallowing dysfunction and/or oral function for feeding
92610 Evaluation of oral and pharyngeal swallowing function
HCPCS Codes for Speech Therapy
G0153 Services performed by a qualified speech-language pathologist in the home health or hospice setting, each 15 minutes
S9128 Speech therapy, in the home, per diem
S9152 Speech therapy, re-evaluation
Other HCPCS codes for Early Intervention Services/Birth to Three
H2014 Skills training and development, per 15 minutes
T1023 Screening to determine the appropriateness of consideration of an individual for participation in a specified program, project or treatment protocol, per encounter
T1027 Family training and counseling for child development, per 15 minutes
T1028 Assessment of home, physical and family environment, to determine suitability to meet patient’s medical needs
T2024 Service assessment/plan of care development, waiver
It is evident that understanding the specific early evaluation program as well as payer guidelines is necessary to ensure accurate billing and appropriate reimbursement for these services. With extensive and updated knowledge about the different types of early intervention services and their codes as well as payer requirements, an experienced medical billing company can help providers overcome the unique challenges reporting these services on claims.