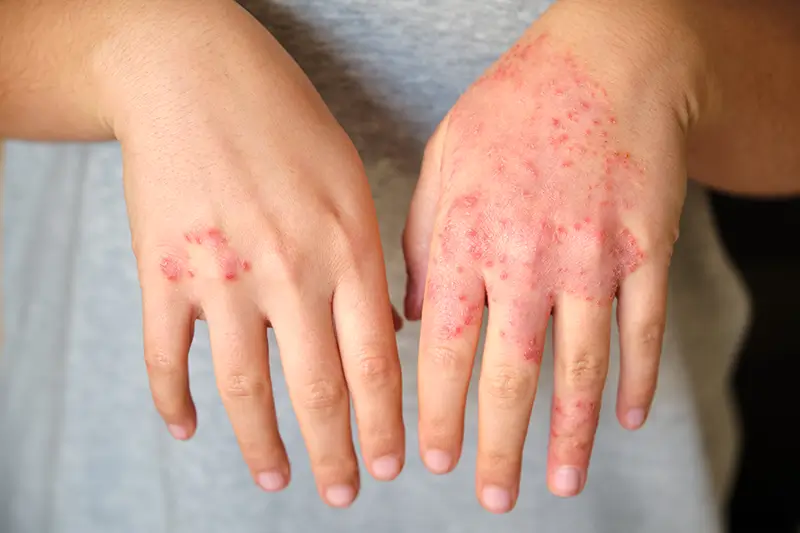
Regarded as a chronic inflammatory disease, dermatomyositis affects the muscles and skin. It can affect adults and children and is most commonly seen in females than males. Accurate and compliant medical billing and coding is critical not only for appropriate reimbursement but also for quality patient care. Let us see how to code for dermatomyositis using the latest ICD-10 codes. It is important to follow the proper rheumatology coding guidelines, and apply relevant CPT codes for rheumatology evaluation.
Ensure accurate billing for dermatomyositis and other autoimmune disorders.
ICD-10 Codes for Dermatomyositis
When coding for dermatomyositis, choosing the correct ICD-10 codes is essential for proper claim submission and data tracking. The primary code for dermatomyositis falls under category M33 – Dermatopolymyositis. Here are the most commonly used ICD-10 codes for dermatomyositis:
- M33 Dermatopolymyositis
- M33.0 Juvenile dermatomyositis
- M33.00 …… organ involvement unspecified
- M33.01 …… with respiratory involvement
- M33.02 …… with myopathy
- M33.03 …… without myopathy
- M33.09 …… with other organ involvement
- M33.1 Other dermatomyositis
- M33.10 …… organ involvement unspecified
- M33.11 …… with respiratory involvement
- M33.12 …… with myopathy
- M33.13 …… without myopathy
- M33.19 …… with other organ involvement
- M33.2 Polymyositis
- M33.20 …… organ involvement unspecified
- M33.21 …… with respiratory involvement
- M33.22 …… with myopathy
- M33.29 …… with other organ involvement
- M33.9 Dermatopolymyositis, unspecified
- M33.90 …… organ involvement unspecified
- M33.91 …… with respiratory involvement
- M33.92 …… with myopathy
- M33.93 …… without myopathy
- M33.99 …… with other organ involvement
It is important to document whether the condition is juvenile or adult-onset and whether there is muscle involvement (myopathy) or not. For example, if a patient presents with classic symptoms of dermatomyositis, confirmed by clinical and laboratory evaluation, and has associated myopathy, the correct code would be M33.11. Additional diagnosis codes may be required for manifestations or complications, such as:
- J84.10 – Pulmonary fibrosis, unspecified
- M79.1 – Myalgia
- R63.0 – Anorexia
- R25.1 – Tremor
Rheumatology Coding Guidelines
Coding in rheumatology requires a clear understanding of how autoimmune diseases are documented, diagnosed, and treated. Rheumatology coding guidelines emphasize the importance of:
- Specificity – Use the most specific ICD-10 codes available.
- Manifestations and complications – Always code secondary manifestations such as lung involvement, vasculitis, or skin ulcers.
- Medical necessity – Ensure that documentation supports the diagnosis and medical necessity of diagnostic tests, biologics, or immunosuppressive treatments.
- Chronic vs. acute – Distinguish between chronic conditions, flares, and new-onset symptoms.
- Capture chronicity – Document whether the condition is stable, worsening, or in remission.
- Utilize modifiers when needed – Especially in repeat services or bilateral procedures.
Documentation should include symptom onset and progression, physical exam findings (e.g. muscle weakness, skin rash), diagnostic results (e.g. muscle biopsy, elevated CK, EMG findings), associated comorbidities and response to therapy.
CPT Codes for Rheumatology Evaluation
Evaluation and management (E/M) codes are fundamental in rheumatology billing, especially for complex autoimmune disorders like dermatomyositis. The CPT codes for rheumatology evaluation include both new and established patient visit codes based on complexity and time spent. Here are the commonly used CPT codes for E/M services:
CPT codes for rheumatology evaluation
- 99202–99205 – New patient visits
- 99212–99215 – Established patient visits
If a rheumatologist conducts a comprehensive initial evaluation with coordination of care, labs, and imaging, a high-level new patient code like 99204 or 99205 may be applicable.
Additional Rheumatology CPT Codes
If the rheumatologist performs additional procedures, such as aspiration, injections, or interpretation of diagnostic tests, you may also need to use:
- 20610 – Arthrocentesis, aspiration, or injection, major joint
- 96372 – Therapeutic, prophylactic, or diagnostic injection (e.g., for administering steroids or biologics)
- 95860–95870 – Electromyography (EMG) studies
- 88172 – Cytopathology, evaluation of fine needle aspiration
For Laboratory Tests Ordered
- 82550 – Creatine kinase (CK), for muscle involvement
- 86376 – ANA, if an autoimmune component is suspected
To accurately code for dermatomyositis you need precision, clinical insight, and must ensure proper adherence to ICD-10 and CPT coding standards. As autoimmune conditions grow in complexity and treatment options expand, it is more important than ever to stay updated on rheumatology coding guidelines and ensure that documentation fully supports the services rendered. For accurate and efficient medical coding in rheumatology, continuous education and collaboration between clinicians and coders is key.
Maximize your medical practice success with our expert medical billing services!