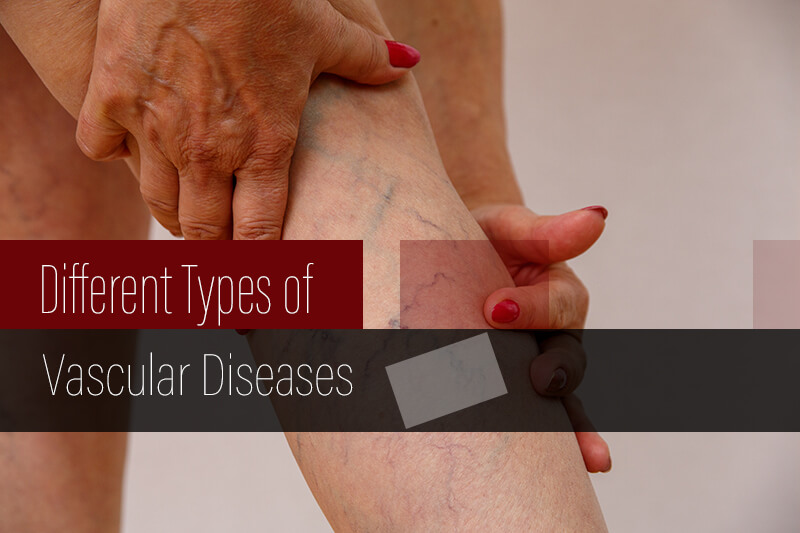
Peripheral vascular diseases are conditions affecting the circulatory system, or system of blood vessels. These range from diseases of the arteries, veins and lymph vessels to blood disorders that affect circulation. These disorders affect blood flow through the arteries and/or the veins, most commonly the legs. However, the location of the pain will depend on the site of the narrowed or clogged artery. Vascular surgeons treating patients with health concerns ranging from life-threatening conditions like abdominal aortic aneurism to minor conditions like varicose veins, have to document all the diagnostic test results and any clinical findings that support the treatments provided. Vascular medical coding involves reporting the condition and treatments provided using the right diagnosis and procedure codes on the medical claims.
Peripheral vascular diseases are caused by blockage of arteries. Key factors that can increase the risk of getting a vascular disease include high blood pressure, gender, family history, genetics, poor physical activity, overweight or obesity, smoking and stress.
Symptoms can vary depending on the type of vascular disease. Common symptoms include leg pain or cramps with activity, high blood pressure, congestive heart failure and abnormal kidney function, leg and foot cramps, numbness, tingling, discoloration, pain in the arms, hands, legs and feet, shortness of breath, chest pain, and dizziness.
ICD-10 Codes for Vascular Diseases
Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm
- I71 Aortic aneurysm and dissection
- I71.3 Abdominal aortic aneurysm, ruptured
- I71.4 Abdominal aortic aneurysm, without rupture
- I71.5 Thoracoabdominal aortic aneurysm, ruptured
- I71.6 Thoracoabdominal aortic aneurysm, without rupture
- I71.8 Aortic aneurysm of unspecified site, ruptured
- I71.9 Aortic aneurysm of unspecified site, without rupture
- I72 Other aneurysm
- I72.8 Aneurysm of other specified arteries
Atherosclerosis
- I70 Atherosclerosis
- I70.0 Atherosclerosis of aorta
- I70.1 Atherosclerosis of renal artery
- I70.2 Atherosclerosis of native arteries of the extremities
- I70.3 Atherosclerosis of unspecified type of bypass graft(s) of the extremities
- I70.4 Atherosclerosis of autologous vein bypass graft(s) of the extremities
- I70.5 Atherosclerosis of nonautologous biological bypass graft(s) of the extremities
- I70.6 Atherosclerosis of nonbiological bypass graft(s) of the extremities
- I70.7 Atherosclerosis of other type of bypass graft(s) of the extremities
- I70.8 Atherosclerosis of other arteries
- I70.9 Other and unspecified atherosclerosis
- I70.90 Unspecified atherosclerosis
- I70.91 Generalized atherosclerosis
- I70.92 Chronic total occlusion of artery of the extremities
Peripheral artery disease
- I73.89 Other specified peripheral vascular diseases
- I73.9 Peripheral vascular disease, unspecified
Blood clots in veins
- I82.9 Embolism and thrombosis of unspecified vein
- I82.90 Acute embolism and thrombosis of unspecified vein
- I82.91 Chronic embolism and thrombosis of unspecified vein
Blood clotting disorders
- D68.8 Other specified coagulation defects
- D68.9 Coagulation defect, unspecified
Buerger’s disease
- I73.1 Thromboangiitis obliterans [Buerger’s disease]
Lymphedema
- I89 Other noninfective disorders of lymphatic vessels and lymph nodes
- I89.0 Lymphedema, not elsewhere classified
Carotid Artery Disease/Carotid Artery Stenosis
- G45.1 Carotid artery syndrome (hemispheric)
Chronic Venous Insufficiency
- I87.2 Venous insufficiency (chronic) (peripheral)
Intestinal Ischemic Syndrome
- K55.05 Acute (reversible) ischemia of intestine, part unspecified
- K55.051 Focal (segmental) acute (reversible) ischemia of intestine, part unspecified
- K55.052 Diffuse acute (reversible) ischemia of intestine, part unspecified
- K55.059 Acute (reversible) ischemia of intestine, part and extent unspecified
Deep Vein Thrombosis
- I82.40 Acute embolism and thrombosis of unspecified deep veins of lower extremity
- I82.401 Acute embolism and thrombosis of unspecified deep veins of right lower extremity
- I82.402 Acute embolism and thrombosis of unspecified deep veins of left lower extremity
- I82.403 …. bilateral
- I82.409 Acute embolism and thrombosis of unspecified deep veins of unspecified lower extremity
Varicose Veins
- I83 Varicose veins of lower extremities
- I83.0 Varicose veins of lower extremities with ulcer
- I83.1 Varicose veins of lower extremities with inflammation
- I83.2 Varicose veins of lower extremities with both ulcer and inflammation
- I83.8 Varicose veins of lower extremities with other complications
- I83.9 Asymptomatic varicose veins of lower extremities
Pulmonary Embolism
- I26 Pulmonary embolism
- I26.0 Pulmonary embolism with acute cor pulmonale
- I26.01 Septic pulmonary embolism with acute cor pulmonale
- I26.02 Saddle embolus of pulmonary artery with acute cor pulmonale
- I26.09 Other pulmonary embolism with acute cor pulmonale
- I26.9 Pulmonary embolism without acute cor pulmonale
- I26.90 Septic pulmonary embolism without acute cor pulmonale
- I26.92 Saddle embolus of pulmonary artery without acute cor pulmonale
- I26.93 Single subsegmental pulmonary embolism without acute cor pulmonale
- I26.94 Multiple subsegmental pulmonary emboli without acute cor pulmonale
- I26.99 Other pulmonary embolism without acute cor pulmonale
- I26.0 Pulmonary embolism with acute cor pulmonale
Raynaud’s Phenomenon
- I73.0 Raynaud’s syndrome
- I73.00 …. without gangrene
- I73.01 …. with gangrene
Thoracic Aortic Aneurysm
- I71.1 Thoracic aortic aneurysm, ruptured
- I71.2 Thoracic aortic aneurysm, without rupture
Vasculitis
- L95 Vasculitis limited to skin, not elsewhere classified
- L95.0 Livedoid vasculitis
- L95.1 Erythema elevatum diutinum
- L95.8 Other vasculitis limited to the skin
- L95.9 Vasculitis limited to the skin, unspecified
Renovascular Hypertension
- I15.0 Renovascular hypertension
Vascular Dementia
- F01 Vascular dementia
- F01.5 Vascular dementia
- F01.50 …. without behavioral disturbance
- F01.51 …. with behavioral disturbance
- F01.5 Vascular dementia
Thrombophilia
- D68.5 Primary thrombophilia
- D68.51 Activated protein C resistance
- D68.52 Prothrombin gene mutation
- D68.59 Other primary thrombophilia
- D68.6 Other thrombophilia
- D68.61 Antiphospholipid syndrome
- D68.62 Lupus anticoagulant syndrome
- D68.69 Other thrombophilia
Klippel-Trenaunay syndrome (KTS)
- Q87.2 Congenital malformation syndromes predominantly involving limbs
May-Thurner syndrome (MTS)
- I87.1 Compression of vein
Vasospastic disorders
- I67.84 Cerebral vasospasm and vasoconstriction
Diagnosis procedures may involve Angiogram, Ankle-brachial index (ABI), Magnetic resonance angiography (MRA), Reactive hyperemia test, Vascular ultrasound, Catheter angiography, CT angiography, and MR angiography. Treatment options include medications to improve blood flow, vascular surgery, angioplasty, atherectomy, stent, catheter embolization, physical therapy and making lifestyle changes. Practices can consider utilizing professional medical billing services provided by experienced companies, to handle their claim submission and coding tasks.