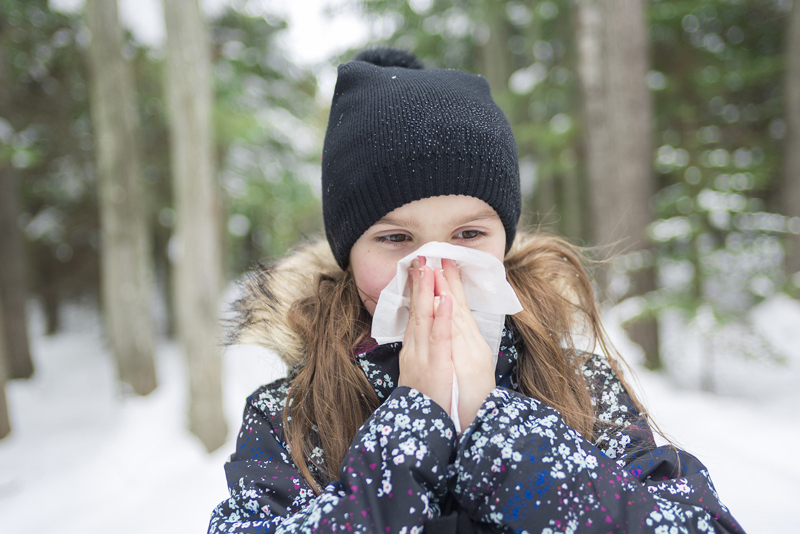
According to recent reports, severe blasts of potentially record cold are expected during across the central, eastern and southern U.S in the days before Thanksgiving, giving millions of people an early preview of winter. And the chilly weather heralds the cold and flu season in the country. Doctors’ offices, ERs and hospitals fill up with patients suffering from a variety of winter illnesses, and as a result, rely on medical billing service providers to manage their coding and claim submission processes. Let’s take a look at four common ailments triggered or worsened by cold weather and their ICD-10 codes.
Common Cold: Acute nasopharyngitis or a cold is a viral infection that can occur year round but is more frequent in the fall and winter months. There are many reasons for this such as start of the school year, the tendency to remain indoors where the dry air dries up the nasal passages and leads to infection, and low humidity levels that allow viruses to survive better. Symptoms of a cold include runny nose or nasal congestion, sore throat, cough, headache, and sometimes, low-grade fever. Children are more susceptible to colds. Symptoms are treated with over-the-counter medications. The condition usually gets worse over 3-5 days and resolves completely in a week to 10 days.
The ICD-10 code to report common cold is:
- J00 – Acute nasopharyngitis (common cold)
This includes: Acute rhinitis; Coryza (acute); Infective nasopharyngitis NOS; Infective rhinitis; Nasal catarrh, acute, and Nasopharyngitis NOS.
Codes adjacent to J00:
- J01 – Acute sinusitis
- J01.0 – Acute maxillary sinusitis
- J01.00 – …… unspecified
- J01.01 – Acute recurrent maxillary sinusitis
- J01.1 – Acute frontal sinusitis
- J01.10 – …… unspecified
- J01.11 – Acute recurrent frontal sinusitis
- J01.2 – Acute ethmoidal sinusitis
- J01.20 – …… unspecified
- J01.21 – Acute recurrent ethmoidal sinusitis
Tips to prevent cold:
- Washing hands often with soap or using a hand santizer
- Wash or disinfect commonly used items, like toys, doorknobs, phones, and faucet handles
- Sneeze into a tissue and covering your mouth when you cough to prevent the virus from spreading
- Getting a flu shot
Acute Bronchiolitis: This is a common lung infection affecting infants and young children. Cases of acute bronchiolitis peak during the winter months. This virus infection causes inflammation and congestion in the small airways of the lung. It begins with symptoms similar to the common cold but progresses to breathing difficulties, wheezing, and frequently, an ear infection (otitis media). Complications of severe bronchiolitis include blue lips, sleep apnea, dehydration and low levels of oxygen. Preventive measures are similar to those for common cold.
The ICD 10 codes for acute bronchiolitis are:
- J21.0 – Acute bronchiolitis due to respiratorysyncytial virus
- J21.1 – Acute bronchiolitis due to humanmetapneumovirus
- J21.8 – Acute bronchiolitis due to other specifiedorganisms
- J21.9 – Acute bronchiolitis, unspecified
The documentation should clearly identify the acuity of the condition, such as whether acute or chronic. The specific causes should also be listed. Any related secondary disease processes should be described.
Strep Throat (Sore Throat): An infection of the pharynx, sore throat is a painful inflammation of the throat. Viruses cause about 90% of throat infections and can spread through coughs and sneezes and unwashed hands that come into contact with fluids from a sick person’s nose or mouth. When it is not viral, infectious pharyngitis can be caused by a bacterium which causes strep throat.
Strep throat or sore throat is one of the most common complaints that physicians see during the cold season. This painful inflammation of the back part of the throat can involve the back portion of the tongue, the roof of the mouth, and the tonsils.
The main symptom of strep throat is a sore throat and pain with swallowing. Symptoms will differ depending on whether the infection is viral or bacterial. Symptoms of pharyngitis include a red throat, runny or stuffy nose, dry cough, hoarseness, and redness of the eyes. Strep throat is characterized by fever, body ache, headache, enlarged tonsils with white spots, and swollen, tender lymph nodes.
Viral pharyngitis usually is treated by treating the symptoms. Treatment measures that reduce the discomfort associated with throat infection include rest, medication for throat pain, drinking plenty of warm fluids, using a cool mist vaporizer to relieve throat dryness, etc. Patients with strep throat will also be prescribed antibiotics to prevent complications. However, in most cases, viral and strep pharyngitis resolve completely without complications.
The ICD-10 codes for pharyngitis are:
- J02.0– Streptococcal pharyngitis
- J02.8– Acute pharyngitis due to other specified organisms
- J02.9 – Acute pharyngitis, unspecified
- J31.1 – Chronic nasopharyngitis
- J31.2 – Chronic pharyngitis
To determine the correct ICD-10-CM code, the documentation should include: sore throat and the absence of other symptoms; physical exam findings, and positive rapid strep test.
Influenza (Flu): A respiratory illness, flu is more common in winter. The flu virus lives longer indoors as the air is less humid than outside. It is highly contagious as people have closer contact when they spend more time indoors. Symptoms include fever, chills, cough, muscle aches, congestion, runny nose, headache and fatigue. Adults can also experience breathing difficulties, while children can have additional symptoms such as gastrointestinal symptoms, such as nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea. Early detection can prevent spread of symptoms and possible treat the condition before it gets worse. Influenza A and influenza B account for seasonal epidemics in the United States every winter. Type C usually causes mild respiratory illness.
Various options are available to treat flu. Antivirals such as Tamiflu and Relenza can help stop the virus from multiplying in a person’s body. Headache and body pain can be treated with pain relief medication.
Influenza coding covers the signs and symptoms of flu, the vaccination, the disease and its complications.
The ICD-10 code to report flu is:
- J10.1– Influenza due to other identified influenza virus with other respiratory manifestations.
Other flu codes:
- J09 – Influenza due to certain identified influenza viruses
- J10 – Influenza due to other identified influenza virus
- J11– Influenza due to unidentified influenza virus
- J12– Viral pneumonia, not elsewhere classified
- J13– Pneumonia due to Streptococcus pneumoniae
- J14– Pneumonia due to Hemophilus influenzae
- J15– Bacterial pneumonia, not elsewhere classified
- J16– Pneumonia due to other infectious organisms, not elsewhere classified
- J17– Pneumonia in diseases classified elsewhere
- J18– Pneumonia, unspecified organism
There are also various codes to report the signs and symptoms of flu:
- fever (R50.9)
- muscle pain (M79.1)
- fatigue (R53.83)
- cough (R05)
- shortness of breath (R06.02)
- sneezing (R06.7)
- loss of appetite (R63.0)
- headache (R51)
- nasal congestion (R09.81)
- ear pain (H92.0-)
- sepis (A41.9)
The code for getting the flu vaccination is Z23.
As they focus on their patients, outsourced medical billing and coding services are a great option for physicians to ensure accurate medical coding, which is indispensable for proper and timely payment for services rendered.
View our infographic
12 ICD-10 Codes to Report Common Winter-Related Accidents and Conditions