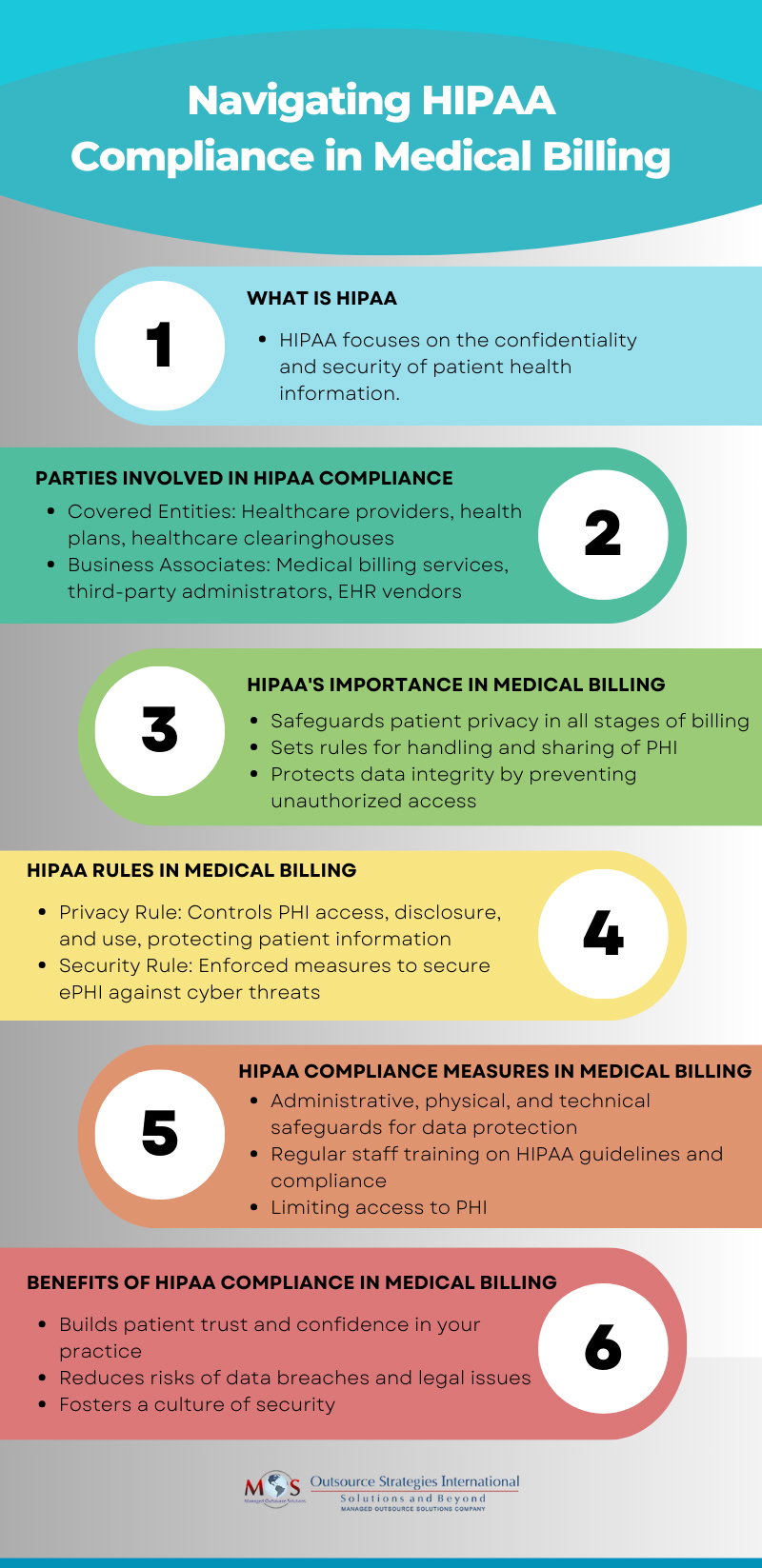
HIPAA, the acronym for the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act, is a complex set of regulations aimed at protecting patients’ sensitive health information. Covered entities, including healthcare providers and insurance companies along with their business associates like medical billing services access protected health information (PHI). As a result, they must comply with HIPAA regulations governing the use, disclosure, and storage of patient health records. Compliance with HIPAA in medical billing is about safeguarding patients’ privacy and confidentiality during the billing process.
Why HIPAA Matters in Medical Billing
Medical billing involves submitting claims to insurance companies to get paid for healthcare services provided to patients. However, the process is more than that – it involves handling of electronic Protected Health Information (ePHI) during the pre, during, and post-claim submission stages. HIPAA ensures that PHI is handled with the highest standards of security throughout these stages.
The medical billing “journey” typically kicks off with a patient registering at a healthcare facility by providing their demographic and insurance details. Insurance eligibility verification is then performed to confirm the patient’s benefits eligibility. This process clarifies copays, coinsurance, and deductibles. Following this, the claim is prepared by translating all of the medical data into billable information. After submission, claims require tracking as well as potential corrections and denials handling.
Medical billing is a series of transactions that can span several months. Healthcare organizations and their business associates need to comply with the requirements of HIPAA during all these stages of the medical billing process.

HIPAA Regulations in Billing
HIPAA comprises two essential regulations: Privacy and Security. The Privacy Rule governs access to patient data, preventing mishandling of sensitive information. The Security Rule centers on safeguarding electronic health records from cyber threats, ensuring their continual protection.
Protecting patient information in billing requires ensuring compliance with the Privacy Rule for oral and written communications as well as with the Security Rule for electronic transactions.
Compliance with the Privacy Rule and Security Rule
As Business Associates under HIPAA, medical billing companies have access to the following PHI:
- Past and current medical conditions and treatment information
- Amount that patients or their insurance companies paid for treatment
- The patient’s healthcare provider’s location
When it comes to the Privacy Rule, medical billing services and other parties involved in the billing process must understand the General Principles of Uses and Disclosures for PHI, the Minimum Necessary Standard, and individuals’ rights to access and correct any information maintained about them.
The Security Rule directly relates to billing companies and their responsibility to safeguard accessed PHI. These companies must enforce administrative, physical, and technical measures to uphold the confidentiality, availability, and integrity of PHI.
The necessary safeguards for protecting patient information in billing are:
Physical safeguards: Physical safeguards such as alarm systems, security systems, and locking areas to ensure security of offices/locations where PHI or ePHI may be stored or maintained.
Technical safeguards: Technical cybersecurity safeguards such as strong passwords, firewalls, encryption, and data backup to protect the cybersecurity of ePHI maintained by the company.
Administrative safeguards: This includes documentation of the policies and procedures of the security safeguards that the billing company has in place including employee training on these aspects to ensure that they are being properly implemented.

Get Comprehensive Information on Medical Billing Codes and Standards
HIPAA and Medical Billing Practices
HIPAA compliance is a shared responsibility among all entities involved in the billing process. Whether it’s your practice staff, hospital teams, medical billing services, or insurance companies, ensuring compliance is a joint effort. In addition to reducing risks of data breaches and associated legal consequences, adhering to HIPAA guidelines upholds patient trust in your practice. It reassures them that their personal health information is securely maintained and managed.

Ready to enhance your medical billing with HIPAA compliance? Discover our expert strategies and services.
View our infographic on HIPAA Compliance in Medical Billing