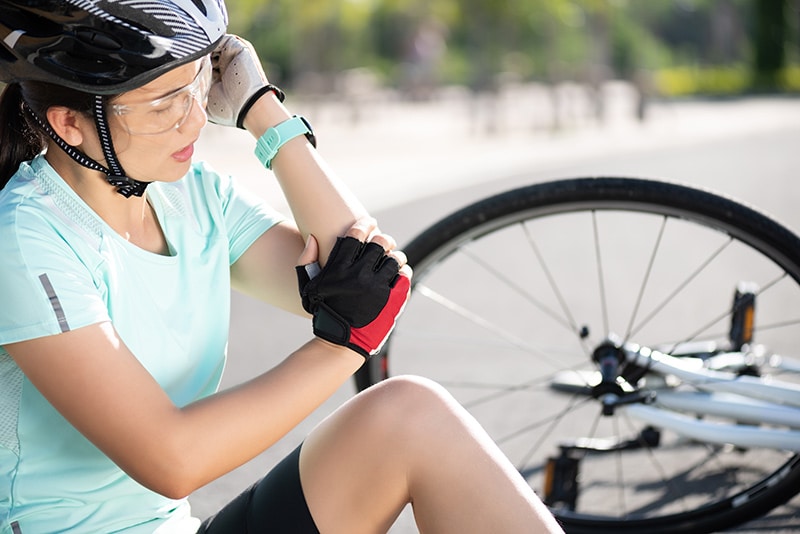
As discussed in our last blog, cycling provides great benefits and is a great exercise to stay fit. However, cycle riders may have to face injuries and pain as well. Cycling injuries are mainly treated by orthopedic specialists, physical therapists, sports medicine specialists and chiropractors. An experienced medical coding company can assist these specialists with ICD-10 coding of such injuries on their reimbursement claims.
Most cycling injuries can be the result of poor bike fit, over speed, improper riding techniques or even poor posture. Some of these injuries are preventable too. Traumatic and overuse injuries are common in cyclists participating in athletic forms of bicycling. More and more people are now bicycling to commute, exercise, or for fun. Just as other motorized vehicles, bicycles or bikes on the roadway have the same rights and responsibilities. To avoid injuries, it is also important for the riders to be aware of bicycle safety tips and rules of the road.
Here are some common bicycle injuries and related ICD-10 codes.
Head Injury and Concussion
In bicycle crashes, head injury is the leading cause of death and permanent disabilities. According to the Consumer Product Safety Commission (CPSC), a majority of the 80,000 cycling-related head injuries treated in emergency rooms each year are brain injuries. Concussion caused by severe head trauma is also a common injury in cycling where the brain moves violently within the skull. It can happen in a fall, a bang to the head or whiplash. Head injuries can be limited to a great extent by wearing bike helmets.
- S06.0 Concussion
- S06.0X Concussion
- S06.0X0 Concussion without loss of consciousness
- S06.0X1 Concussion with loss of consciousness of 30 minutes or less
- S06.0X9 Concussion with loss of consciousness of unspecified duration
- S06.0X Concussion
- S09.8 Other specified injuries of head
- S09.8XXA …… initial encounter
- S09.8XXD …… subsequent encounter
- S09.8XXS …… sequela
- S09.9 Unspecified injury of face and head
- S09.90 Unspecified injury of head
Shoulder Injuries
Bike crashes may lead to serious shoulder injuries such as clavicle fracture, shoulder separation or acromio-clavicular (AC) joint injury and rotator cuff tears. Clavicle fracture or broken collarbone refers to break to either the collarbone or the neck of the arm bone. In most cases, injuries to the acromioclavicular (AC) joint or shoulder separation may recover fully without surgery. AC joint attaches the shoulder to the rest of the body. Rotator cuff tears can be result of a hard fall on the shoulder. While small cuff tears can be treated with physiotherapy, larger tears may require surgery.
- S42.0 Fracture of clavicle
- S42.00 Fracture of unspecified part of clavicle
- S42.001 Fracture of unspecified part of right clavicle
- S42.002 Fracture of unspecified part of left clavicle
- S42.009 Fracture of unspecified part of unspecified clavicle
- S42.01 Fracture of sternal end of clavicle
- S42.011 Anterior displaced fracture of sternal end of right clavicle
- S42.012 Anterior displaced fracture of sternal end of left clavicle
- S42.013 Anterior displaced fracture of sternal end of unspecified clavicle
- S42.014 Posterior displaced fracture of sternal end of right clavicle
- S42.015 Posterior displaced fracture of sternal end of left clavicle
- S42.016 Posterior displaced fracture of sternal end of unspecified clavicle
- S42.00 Fracture of unspecified part of clavicle
- S43.42 Sprain of rotator cuff capsule
- S43.421 Sprain of right rotator cuff capsule
- S43.422 Sprain of left rotator cuff capsule
- S43.429 Sprain of unspecified rotator cuff capsule
Ulnar Neuropathy
Also referred to as hand numbness or handlebar palsy, this is an overuse or repetitive stress condition that affects cyclists. The condition is caused by direct pressure on the ulnar nerve of the hand and wrist by pressing on the handlebars continuously for long periods of time. Often, non-surgical treatments such as rest or anti-inflammatory medications are recommended for this condition.
- G56.2 Lesion of ulnar nerve
- G56.20 …… unspecified upper limb
- G56.21 …… right upper limb
- G56.22 …… left upper limb
- G56.23 …… bilateral upper limbs
Pudendal Neuropathy
Pudendal or bicycle seat neuropathy is another common cycling injury. Sitting in the saddle too long can cause chronic pelvic pain. Major symptom is numbness or impotence after cycling. To reduce the risk of this condition, riders are recommended to take regular rest breaks and time off from cycling.
- G58 Other mononeuropathies
- G58.0 Intercostal neuropathy
- G58.7 Mononeuritis multiplex
- G58.8 Other specified mononeuropathies
- G58.9 Mononeuropathy, unspecified
Knee Pain
Knee pain is common with cyclists. Poor posture is the major reason for cycling knee pain. To avoid stress to the knee, riders have to fix the cleat positions the right way. Knee pain in athletes can be related to patellofemoral pain syndrome or runner’s knee, which is the pain under and around the kneecap. Key symptoms are crackling noises and sensations in the knee joint.
- M25.56 Pain in knee
- M25.561 Pain in right knee
- M25.562 Pain in left knee
- M25.569 Pain in unspecified knee
- M22.2 Patellofemoral disorders
- M22.2X Patellofemoral disorders
- M22.2X1 …… right knee
- M22.2X2 …… left knee
- M22.2X9 …… unspecified knee
- M22.3 Other derangements of patella
- M22.3X Other derangements of patella
- M22.3X1 …… right knee
- M22.3X2 …… left knee
- M22.3X9 …… unspecified knee
- M22.3X Other derangements of patella
Lower Back Pain
Back pain is a common problem in cycling. Spending hours in the same position for a long time can upset the lower back muscles, causing low back pain. Too high saddles will also add stress to your hips when you pedal, leading to lower back pain. It can also be a result of poor spinal health.
- M54.5 Low back pain
Achilles Tendonitis
Cycling often increases the risk of developing Achilles tendonitis, an overuse injury of the Achilles tendon. Left untreated, the injury can result in the tear or rupture of tendons. Treatment may include rest, physical therapy or even surgical repair.
- M76.6 Achilles tendinitis
- M76.60 Achilles tendinitis, unspecified leg
- M76.61 Achilles tendinitis, right leg
- M76.62 Achilles tendinitis, left leg
Muscle Cramps
Riders stress on quad muscles to actually ride the bike. Cycling may cause tight, intense pain in the leg muscle. It is mainly caused by factors such as muscle fatigue, dehydration, electrolyte depletion and low electrolyte levels.
- M62.83 Muscle spasm
- M62.831 …… of calf
- M62.838 Other muscle spasm
- M62.89 Other specified disorders of muscle
- M62.9 Disorder of muscle, unspecified
Documenting and reporting these injuries require key attention, as any errors in codes can lead to claim denials and delays. Practices treating bicycle related injuries can rely on professional medical billing and coding companies to get their claims submitted on time with accurate medical codes. Reliable companies also provide comprehensive insurance verification services as well as accounts receivable collections to boost the revenue of your practice.