Heart murmurs in new born babies are a cause of concern and require immediate attention of a pediatric cardiologist. It is diagnosed by health practitioners during physical examination of the infant. If the heart murmur is abnormal, the patient needs to undergo the following tests:
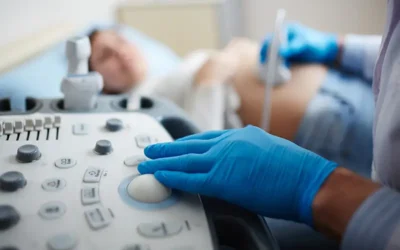
- Echocardiogram: Used to detect the cause of a heart murmur with the help of detailed images of the heart and structures using ultrasound waves.
- Chest X-Ray: Takes the image of the heart, lungs and blood vessels. It shows the size of the heart and the enlargement of the heart shows the cause for abnormal heart murmurs.
- Electrocardiogram (ECG): Helps the pediatric cardiologist to determine the rhythm of the heart and its structure.
- Cardiac Catheterization: The pressure of the heart chamber is measured by inserting a catheter into the vein or artery.
Cardiology medical billing and coding could be a hectic and complex process. The complexities can incur claim denials. Therefore, professional medical billing companies are essential to ensure accurate payment to physicians by maintaining correct documentation standards. A focused approach is required in this regard as cardiology billing is ever changing with additions, deletions and revisions of cardiology codes. Accurate coding involves correct compilation of CPT and diagnostic ICD-10 codes corresponding to specific procedures, treatments and diagnoses.
Cardiovascular CPT codes
- 93224-93278: Cardiovascular Monitoring Services
- 93224: In this procedure, the provider applies an electrocardiographic, or ECG recorder, to a patient for up to 48 hours to detect abnormal heart rates and rhythms. He analyzes, compiles, and interprets the electrocardiographic findings.
- 93225: The physician or other healthcare professional applies an electrocardiograph, or ECG recorder, to a patient for up to 48 hours to help detect abnormal heart rates and rhythms. This service reports the recording only portion of the test.
- 93226: The physician or other healthcare professional applies an electrocardiographic, or ECG recorder, to a patient for up to 48 hours to help detect abnormal heart rates and rhythms. This service reports the scanning analysis and report only portion of the test.
- 93227: In this procedure, the provider reviews and interprets the data from an external electrocardiographic, or ECG recorder, worn by a patient for 48 hours to detect abnormal heart rates and rhythms. He reviews and interprets the electrocardiographic findings.
- 93303-93356: Echocardiography Procedures
-
- 93303: The provider performs a complete transthoracic echocardiography to obtain images of the heart structures through the chest wall in patients born with heart defects. This study includes visualization of heart chambers, valves, blood flow, and cardiac activity. This service has both a professional and technical component.
<li93304: The provider performs a limited or follow-up transthoracic echocardiography to obtain images of the heart through the chest wall in patients born with heart defects. It is a limited examination of a focused clinical concern that does not attempt to evaluate or document all the heart structures included in a complete echo. This service has both a professional and a technical component.
-
- 93306: The provider uses transducers to obtain two-dimensional (2D0 images of the heart structures through the chest wall. He evaluates the anatomy and function of all four heart chambers, valves, adjacent aorta, and wall of the heart. This service has both a professional and a technical component.
- 71045-71555: Diagnostic Radiology ( Diagnostic Imaging) Procedures of the chest
- 71045: In this diagnostic procedure, the provider performs a single radiological view of the chest. He performs this study for the assessment of conditions affecting the chest, its contents, and nearby structures.
- 93593-93598: Cardiac Catheterization for Congenital Heart Defects
- 93593: For a patient born with one or more heart defects and normal native connections, the provider navigates a catheter through the blood vessels to the heart and inserts the catheter into the right side. The provider takes samples to measure blood gases and may perform other measurements.
ICD 10 codes for heart murmur in neonates
- R01 : Cardiac murmurs and other cardiac sounds
- R01.0: Benign and innocent cardiac murmurs
- R01.1 : Cardiac murmur, unspecified
- R01.2 : Other cardiac sounds
- P03.81 : Newborn affected by abnormality in fetal ( intrauterine) heart rate or rhythm
- P03.810: Newborn affected by abnormality in fetal ( intrauterine) heart rate or rhythm before the onset of labor
- P03.819: Newborn affected by abnormality in fetal (intrauterine) heart rate or rhythm, unspecified as to time of onset.
- Q24: Other congenital malformations of heart
- Q24.0: Dextrocardia
- Q24.1: Levocardia
- Q24.2: Cor triatriatum
- Q24.3: Pulmonary infundibular stenosis
- Q24.4: Congenital subaortic stenosis
- Q24.5: Malformation of coronary vessels
- Q24.6: Congenital heart block
- Q24.8: Other specified congenital malformations of heart
- Q24.9: Congenital malformation of heart, unspecified
Outsourcing medical billing and coding can ease the complexities associated with the rules related to diagnostic testing and evaluation procedures. The application of these codes is critical for cardiologists for timely reimbursement of the services provided without compromising patient care.