Predetermination and prior authorization are processes used by insurance companies to determine whether a patient’s treatment or service is covered under their plan. Both processes are components of utilization management (UM) reviews by insurers and must occur before the clinical event or provision of the service. Insurance authorization companies help physician practices effectively navigate the challenges associated with these complex and time-consuming medical insurance coverage requirements.
Understanding the difference between insurance predetermination and the prior authorization process is key to minimizing denials and delays in care.
Get expert assistance with predeterminations and prior authorizations!
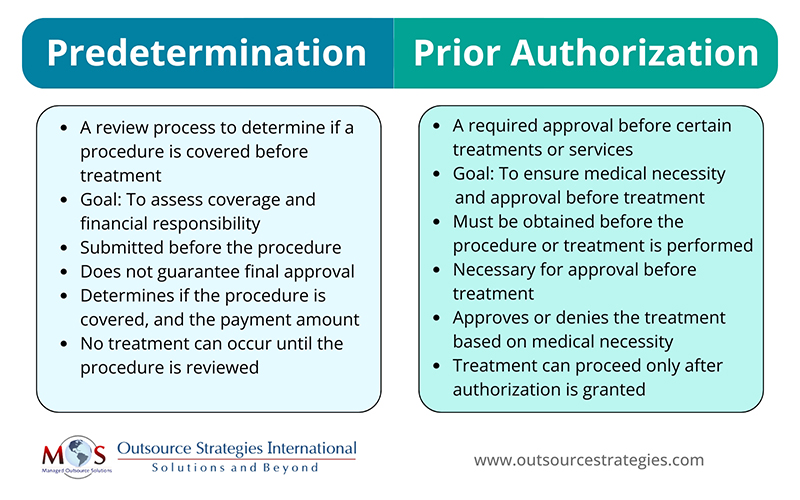
Predetermination of benefits involves healthcare providers submitting details of a proposed medical or dental procedure to the insurer before treatment, which helps to determine coverage, the approved payment amount, and the patient’s financial responsibility. In contrast, prior authorization is a required approval before the patient receives certain treatments and expensive medications.
Let’s take a look at the specifics of preauthorization and predetermination and the differences between these processes.
Understanding Predetermination
Insurance predetermination is a process where the insurance company reviews a recommended medical or dental procedure, treatment or test before it is provided to make sure it meets medical necessity. This process precedes preauthorization and helps the physician clarify whether a specific procedure will be covered under the patient’s insurance policy, helping to avoid unexpected costs in the insurance claim process. Here are some key points about predetermination:
- Typically involves the healthcare provider submitting relevant documentation, including the patient’s medical history and the proposed treatment plan and relevant CPT code, to the insurance company.
- If approved, it confirms the insurance payment and the patient’s financial responsibility in advance, preventing coverage surprises.
- Does not guarantee final approval.
- Is optional, but advised for services that may be considered experimental or investigational when performed for other purposes.
- Not needed for services that are not considered life threatening.
- If a procedure, treatment, or test is not covered, the in-network provider or the member will be responsible for the bill.
Procedures for which predetermination review is recommended include but are not limited to:
- Abdominoplasty
- Implant
- Avastin (Chemotherapy)
- Bariatric Surgery
- Blepharoplasty /
- Ptosis Repair
- Bone Growth Stimulators
- Botox
- Breast MRI
- Breast Reduction
- Brachytherapy
- Cryoablation or Radiofrequency Ablation
- CT Angiogram
- Chelation Therapy
- Dental Implants
- Dental Surgery
- Counterpulsation (EECP)
- Growth Hormone
- Intensity Modulated Radiation Therapy (IMRT)
- Lipectomy/ Liposuction
- Nasal Surgeries
- Peripheral Nerve Vagus Nerve or Spinal Cord Stimulator
- Orthotics
- OATS Procedures
- Panniculectomy
- PET Scans
- Sacroiliac (SI) Joint Injections
- Transplants
- Varicose Vein Procedures
Importance of Predetermination
- Reduces denials: By verifying coverage upfront, we help prevent denials or underpayments due to lack of authorization or insufficient documentation.
- Ensures financial clarity: Patients gain visibility into their coverage and potential costs, allowing them to make informed decisions.
- Speeds up the revenue cycle: With prior approval or clarification, your practice avoids payment delays, ensuring quicker reimbursements and smoother financial operations.
- Enhances patient satisfaction: By providing a transparent process, you reduce patient anxiety about unexpected costs, fostering trust and satisfaction.
Understanding Prior Authorization
Prior authorization (also called preauthorization, prior approval, or precertification) is a process used by insurance companies to determine if a patient is eligible for certain procedures, medications, or tests, which are integral to authorization in healthcare. It assesses whether a service, treatment, prescription drug, or DME is medically necessary.
Treatments and medications that may require prior authorization include:
- Expensive medications and treatments
- Drugs with unsafe interactions or combinations
- Affordable alternative treatments
- Medications prescribed for unique health issues
- Drugs prone to misuse or abuse
- Medical procedures like surgeries, transplants, imaging, and tests
- Behavioral services such as mental health care, psychological testing, and psychiatric care
- Medications used for cosmetic purposes
The insurer will review the requested service or drug to ensure it meets certain criteria:
- Is medically necessary
- Is appropriate and follows up-to-date guidelines for the condition
- Is the most cost-effective option for the patient’s condition
- Will be delivered in the right setting
- Is not being duplicated (e.g., two CT scans ordered by different physicians)
- Is providing benefit for ongoing or recurrent services (e.g., physical therapy)
- Is covered under the patient’s health plan
Health plans have specific rules for prior authorization. Typically, high-cost medications, expensive treatments, outpatient procedures, invasive procedures, durable medical equipment (DME), and imaging scans (CT, MRI, PET) may require pre-certification. Without prior approval, the health plan may not cover the treatment, leaving the patient or provider responsible for the cost.
Requesting prior authorization is typically the provider’s responsibility if the patient is treated by a physician in the plan’s network, though some plans require the patient to request it. Insurance authorization companies handle prior authorizations via phone or web portals, requiring details such as patient demographics, insurance information, physician information, and clinical review.
Within 5-10 business days of receiving the request, the insurer will either:
- Approve or deny the request
- Ask for additional information
- Suggest a less costly but equally effective alternative before approving the original request
While the goal is to ensure cost-effective, safe, and appropriate care, prior authorization can delay treatment, especially for medications prescribed for chronic conditions, potentially slowing patient progress.
What Are the Differences Between Predetermination and Prior Authorization?
How an Insurance Authorization Company can Help
An authorization denial in medical billing can lead to several challenges for both healthcare providers and patients. Denied authorizations can postpone necessary procedures or treatments, affecting patient health and potentially leading to worsened conditions, especially when navigating the complex world of authorization in healthcare. It can result in delayed reimbursements, disrupting the provider’s cash flow and affecting overall revenue.
Leveraging the best insurance authorization companies for doctors can help physicians streamline the process of obtaining predeterminations and prior authorizations. They handle prior authorizations through phone or web portals, ensuring that all necessary details, such as patient demographics, insurance information, physician details, and clinical reviews, are submitted accurately. By acting as intermediaries between healthcare providers and insurance companies, these companies can help ensure that prior authorization requests are processed quickly. They assist in addressing issues such as additional information requests, alternative treatment suggestions, or potential denials. With their expertise in navigating complex insurance requirements, they reduce delays in patient care and reimbursement, making the process smoother for both providers and patients.
Optimize your insurance verification and authorization processes.