Health insurance companies use authorization as a utilization management strategy. Authorizations in medical billing require an evaluation of the medical necessity and cost-of-care implications of specific treatments, tests, and drugs before providers administer them. Denied authorizations can delay patient care and lead to claim rejections, ultimately affecting both revenue and patient satisfaction. Real-time insurance verification solutions for healthcare providers can provide the support needed to obtain authorizations and ensure healthcare services are covered by the patient’s insurance plan before they are provided. There are various types of authorizations in medical billing, each serving a specific purpose in the billing and care process.
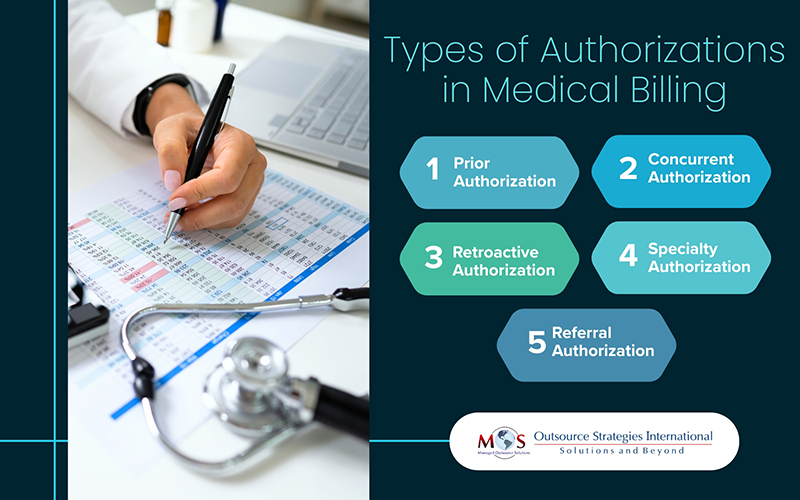
Five Key Types of Authorizations in Medical Billing
Understanding what types of authorizations are required in medical billing and approvals is necessary to navigate them effectively.
- Prior Authorization
Also referred to as Pre-authorization, Preapproval or Pre-certification, Prior Authorization is the most common type of authorization in medical billing. It is the approval required from the health insurance company for covering a service, treatment, or prescription. Pre-authorization is common for complex surgeries, certain diagnostic tests, and specialty medications. Prior authorization is not required if the medical situation is an emergency.
When a specific treatment or prescription drug requires approval as per the patient’s plan, the healthcare provider will submit a request to the insurance company with relevant medical information about the patient’s condition to obtain the approval. The insurer will review the medical necessity documentation and coverage details to approve or deny the request.
Simplify insurance authorization with our support!
Here are some services or procedures for which pre-authorization and eligibility checks may be required:
- admission to a hospital or skilled nursing facility
- planned surgery
- certain imaging tests, like an MRI or CT scan
- specific medications
- Durable medical equipment (DME) like wheelchairs, CPAP/BIPAP machines, prosthetics, and supplies
Prior authorization may be needed for prescription drugs if they:
- have a less expensive generic
- are expensive such as psoriasis and RA medications
- have dangerous side effects
- are used for cosmetic reasons (as with hair growth and wrinkle treatments)
- are used at higher doses than normal
- are dangerous when used in combination with certain drugs
- are used to treat non-life threatening conditions
- have the potential to be misused or abused
If approval for a prescription medication is denied, the provider and patient may be given the option to appeal or select an alternative medication.
Many insurance plans require that medical insurance pre-authorization be secured prior to, or within 14 calendar days of the service being rendered. Beginning the process early is important as coverage will not happen without it. As the insurance authorization process can be time consuming, most physician practices prefer to rely on professional insurance preauthorization services to obtain them.
- Concurrent Authorization
Unlike prior authorization, which is obtained before starting a treatment, Concurrent Authorization is needed during the treatment to ensure that continuing care is medically necessary and that the patient still qualifies for coverage under their insurance plan. It is typically used for services that are extended over a period of time, such as inpatient stays, long-term treatments, or certain types of therapies requiring multiple visits.
Insurance companies use concurrent authorization to ensure that the treatment is still appropriate, effective, and aligned with the patient’s health condition as it evolves. It helps to monitor whether the patient continues to meet the criteria for the services they are receiving. Situations were concurrent authorization comes into play include:
Extended hospital stays: If a patient is admitted to the hospital for a lengthy stay (like a surgery recovery, or treatment for a chronic condition), the insurance company may need to approve each extension of care beyond the initial admission.
Ongoing therapies: Examples include physical therapy, chemotherapy, or other types of ongoing treatments where the patient requires multiple sessions over a period of time.
Home healthcare: Home healthcare services, such as nursing or physical therapy, insurance may need approval for each visit or a set period of treatment.
Obtaining concurrent authorization ensures continued insurance coverage as the treatment progresses. However, if concurrent authorization is delayed or denied, it can cause interruptions in the patient’s care, potentially leading to slower recovery or complications.
- Retroactive Authorization
Prior or pre-authorization involves obtaining approval from the insurer before providing services to the patient. But what happens if a provider is unable to obtain pre-authorization before delivering the services? In certain rare cases and emergencies where pre-authorization is not possible, retroactive authorization may come into play.
Retroactive Authorization allows healthcare providers to seek approval for services that have already been provided. This process involves submitting a request for approval after the treatment has been delivered and the specified time period has passed. It is typically used in situations where prior authorization could not be obtained due to urgent circumstances, such as:
- The patient is unconscious or in an emergency situation, making it impossible for the provider to gather the necessary information for pre-auth.
- The provider doesn’t have enough time to obtain pre-authorization.
- The patient is transitioning between health plans, and services are provided during a period when coverage status is unclear.
- The provider mistakenly believed that prior authorization wasn’t required and proceeded with the service.
- The provider made reasonable efforts to secure prior authorization but was unable to do so.
Retroactive authorization acts as an important safeguard for providers, ensuring they are reimbursed appropriately for services rendered when prior authorization could not be obtained in advance.
- Specialty Authorization
Specialty Authorizations in medical billing refer to prior approvals required for specific types of healthcare services provided by specialists. These authorizations are often necessary for treatments or procedures that fall outside the scope of general or primary care. They ensure that the recommended services are medically necessary and covered under the patient’s insurance plan.
Specialty authorizations aim to control healthcare costs while ensuring patients receive appropriate care. Situations where specialty authorization requirements apply include:
Specialist visits: Referral and authorization might be required for consultations with specialists like cardiologists, dermatologists, or oncologists.
Advanced diagnostics: Tests such as MRIs, CT scans, or genetic testing often require prior approval.
Procedures and surgeries: High-cost procedures, including orthopedic surgeries or fertility treatments, may need authorization.
Therapies: Services like physical therapy, occupational therapy, or speech therapy might require approval for specified durations or sessions.
High-cost medications: Specialty drugs for conditions like cancer, rheumatoid arthritis, or rare diseases typically need pre-authorization.
Failing to secure authorization can result in denied claims and unexpected out-of-pocket expenses for the patient.
- Referral Authorization
A referral is a written order from a primary care physician (PCP), asking the patient to see a specialist or get certain medical services (Heathcare.gov). Insurers use Referral Authorization to confirm that the referral aligns with the patient’s coverage plan.
After the PCP refers the patient to a specialist, they will make a written note of the referral in the patient’s medical records. Depending on the insurance plan, a verbal referral from the PCP will be sufficient. Medical services that may require both a referral and pre-authorization include:
- Consulting a specialist
- Undergoing a medical procedure
- Receiving specialized diagnostic tests
- Having surgery
- Visiting an urgent care center
- Being admitted to a hospital
- Obtaining a second opinion
- Seeing a healthcare provider outside the member’s plan’s network
Healthcare Maintenance Organizations (HMOs) typically require patients to get referrals from their PCP to see specialists within the HMO network, meaning they need an “in-network referral” to access specialized care. In contrast, patients with Point of Service (POS) plans can access medical care outside the network, provided the referral is made by their PCP.
Seeking care from a specialist without a referral or choosing one outside the insurance network typically leaves the patient responsible for most of the treatment costs.
When pre-approval for services or medications is denied, it can cause delays in patient care and financial challenges for healthcare providers. Understanding the common reasons for these denials is crucial for both providers and patients to navigate the process effectively.
Common Reasons Authorizations are Denied in Medical Billing
Getting authorizations is a tedious and complex process. Even for similar medical services, payer-specific authorization requirements can vary significantly, in terms of the criteria for requiring prior authorization, the necessary documentation, and the approval process. This inconsistency often creates challenges for providers navigating the different types of authorizations in medical billing. Here are the typical reasons for prior auth denials:
- Missing or incomplete information in the request.
- Failure to meet the insurance company’s medical necessity criteria.
- Incorrect or mismatched diagnostic or procedural codes.
- Seeking services from an out-of-network provider.
- Not obtaining prior authorization when it’s required.
- Lack of documented attempts at less costly or alternative treatments.
- Requesting services that are not covered by the patient’s plan.
- The prior authorization approval has expired.
- Submitting duplicate requests without addressing previous denials.
- Administrative errors in the submission.
- Not participating in a required peer-to-peer review.
Careful review, understanding insurance policies, and clear communication can help reduce the chances of denials.
Expert Support for Authorizations can make a Difference
The American Medical Association (AMA) and Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) are constantly engaged in efforts to improve prior authorization through research, practice tools, and reform resources. Outsourcing is a practical way to navigate the different types of authorizations and avoid authorization denials in medical billing.
In a professional insurance authorization company, experts leverage digital tools and AI-powered processes to manage the process, ensuring better outcomes for patients, providers, and payers alike. Leveraging prior authorization services for specialty medical treatments is an ideal way to overcome the challenges associated with obtaining authorizations. Experts can help your practice streamline the time-consuming and complex process and minimize claim denials through accurate insurance verification, improving care delivery and patient satisfaction.
Get in touch with our experts now for seamless approvals and faster reimbursements!