Accurate HCC coding is essential for anticipating future healthcare financial resources, so that physicians can claim appropriate reimbursement. The HCC model is a value-based payment model implemented in 2004 to assign Risk Adjustment Factor (RAF) to each Medicare patient to estimate the probable costs that the patient may incur during his/her lifetime. It helps the health practitioners to effectively communicate with the patient, the complexity of his or her health status. HCC codes are directly tied to ICD-10 codes and HCC coefficients depend upon the patient category.
The risk scores are assigned based on demographic factors such as age, gender and ethnicity.
Why transplant status HCC coding is important
- Chronic conditions of the patient like heart disorder, diabetes and cancer need to be actively treated as it may seriously affect the patient’s health. Status codes are necessary to help the physicians identify the significant medical events that the patient experienced in the past.
- Enables confirmed diagnosis which is important to treat a patient on a long-term basis and anticipate the required patient care in the future.
- Chronic conditions are part of the patient history and there are chances that it may not necessarily treated at every encounter. This increases the chances of missing out on reporting the appropriate codes.
- Erroneous documentation of complex diagnosis can lead to under reporting during claim submission for reimbursement.
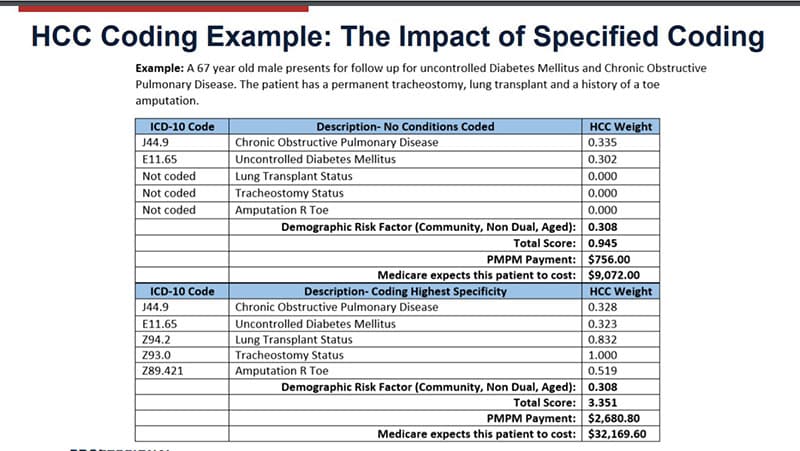
The figure below shows the cost analysis when transplant status is correctly coded:
Important transplant status codes
Identifying whether the patient has a history of organ or tissue transplant is the pre-requisite to capture transplant status codes. Transplant patients need close monitoring and superior care as they require long-term medication. Physician coding companies can assist with error-free documentation of transplant status HCC codes as these codes are determinant of the cost-metrics. Failing to appropriately report transplant status codes could lead to substantial loss of revenue opportunities.
- Z94 Organ transplant status Category Z94 codes identify post-transplant status when there are no complications of the transplanted organ. A code from this category is appropriate as an additional code when a post-organ transplant patient presents for treatment of a condition that does affect the function of the transplanted organ.
- Z94.0 Kidney transplant status
Includes: organ or tissue replaced by heterogenous or homogenous transplant
Excludes 1: Complications of transplanted organ or tissue.
Excludes 2: Presence of vascular grafts.- Z94.1 Heart transplant status
Excludes1: artificial heart status (Z95.812) Heart-valve replacement status (Z95.2-Z95.4)
- Z94.2 Lung transplant status
Includes: organ or tissue replaced by heterogenous or homogenous transplant.
Excludes1: Complications of transplanted organ or tissue.
Excludes2: Presence of vascular grafts.- Z94.3 Heart and Lungs Transplant Status
Includes: organ or tissue replaced by heterogenous or homogenous transplant.
Excludes1: Complications of transplanted organ or tissue.
Excludes2: Presence of vascular grafts.- Z94.4 Liver transplant status
Includes: organ or tissue replaced by heterogenous or homogenous transplant.
Excludes1: Complications of transplanted organ or tissue.
Excludes2: Presence of vascular grafts.- Z94.5 Skin transplant status
Includes: organ or tissue replaced by heterogenous or homogenous transplant.
Excludes1: Complications of transplanted organ or tissue.
Excludes2: Presence of vascular grafts.- Z94.6 Bone transplant status
Includes: organ or tissue replaced by heterogenous or homogenous transplant.
Excludes1: Complications of transplanted organ or tissue.
Excludes2: Presence of vascular grafts.- Z94.7 Corneal transplant status
Includes: organ or tissue replaced by heterogenous or homogenous transplant.
Excludes1: Complications of transplanted organ or tissue.
Excludes2: Presence of vascular grafts.- Z94.8 Other transplanted organ and tissue status
Includes: organ or tissue replaced by heterogenous or homogenous transplant.
Excludes1: Complications of transplanted organ or tissue.
Excludes2: Presence of vascular grafts.- Z94.81 Bone marrow transplant status
- Z94.82 Intestine transplant status
- Z94.83 Pancreas transplant status
- Z94.84 Stem cells transplant status
- Z94.9 Transplanted organ and tissue status, unspecified.
Includes: organ or tissue replaced by heterogenous or homogenous transplant.
Excludes1: Complications of transplanted organ or tissue.
Excludes2: Presence of vascular grafts.
Unlike other code sets, HCC coding requires additional precision. Medical billing and coding companies assist health practitioners to efficiently manage their revenue cycle. Clinical documentation is enhanced by adhering to reimbursement schedules and compliances.