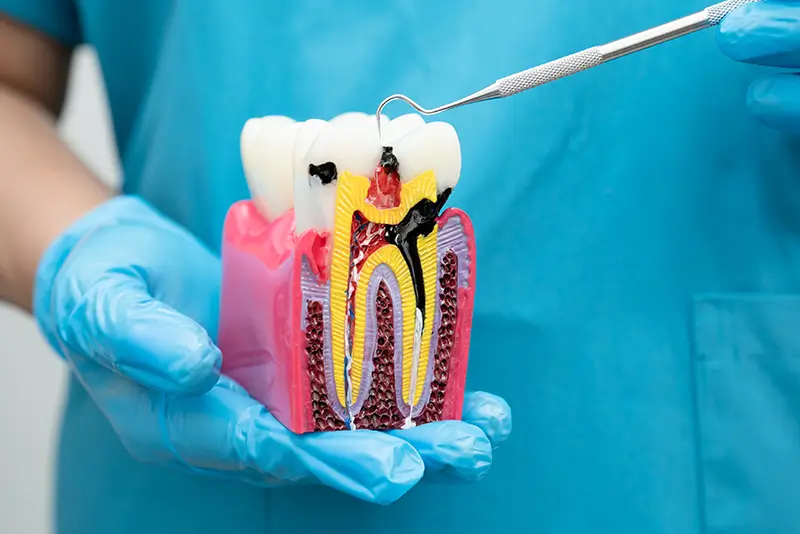
A root canal is one of the most common endodontic treatments performed in dental practices. It addresses infected or inflamed dental pulp – the soft inner layer of the tooth, aiming to restore the health of an infected tooth, but to also preserve the natural appearance of your smile. CDT codes are revised annually, and effective January 1, 2024, dental practices need to use CDT 2024 in claims submissions. Dental billing services are available to assist endodontists in filing dental claims for timely and appropriate reimbursement. This post discusses the steps in the root canal procedure, root canal billing considerations, and the relevant 2024 CDT codes.
Take the pain out of claim submission with our dental billing services!
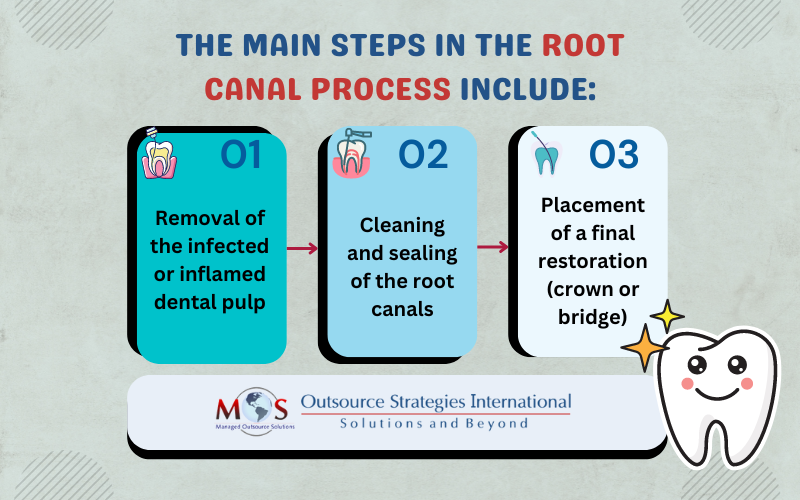
Steps in the Root Canal Process
- Imaging: A 3D X-ray image is taken of the tooth requiring root canal to understand the features of the tooth’s structure.
- Administering local anesthesia: The inflamed region of the tooth is numbed with local anesthesia to ensure painless treatment.
- Creating a dental dam: A dental dam is placed to isolate the teeth or area being worked on from the rest of the mouth to prevent saliva and oral bacteria from contaminating the treatment site.
- Drilling of the affected tooth: A small hole is drilled along the biting surface of the tooth or into the back of the tooth to access the dead pulp chamber.
- Removal of dead pulp tissues and nerves: The damaged tissues and nerves are removed using specialized dental tools.
- Disinfecting: The affected tooth is disinfected along the canals and the inner portion. This is the most important step of the procedure.
- Shaping the affected area for filling and sealing: Flexible root canal tools are inserted along the canals of the teeth to shape the area for applying filler and sealer.
- Application of filling: The filling of the root canal is done using Gutta-Percha Cones or sealers or a combination of both. A post may be inserted to hold the temporary or permanent filling in place.
Here is a more detailed description of the root canal treatment:
2024 CDT Codes for Root Canal Therapy
Endodontic Therapy (Including Treatment Plan, Clinical Procedures and Follow-Up Care)
Endodontic therapy includes primary teeth without succedaneous teeth and permanent teeth. Complete root canal therapy, pulpectomy, is part of root canal therapy. It also includes all appointments necessary to complete treatment; also includes intra-operative radiographs. It does not include diagnostic evaluation and necessary radiographs/diagnostic images.
The CDT codes for endodontic therapy are:
D3310 endodontic therapy, anterior tooth (excluding final restoration). This code encompasses the treatment of the dental pulp and root canal system of a front tooth, excluding the final restoration.
D3320 endodontic therapy, premolar tooth (excluding final restoration)
D3330 endodontic therapy, molar tooth (excluding final restoration)
D3331 treatment of root canal obstruction; non-surgical access
D3332 incomplete endodontic therapy; inoperable, unrestorable or fractured tooth
D3333 internal root repair of perforation defects
To reduce denials, claims should be submitted with a narrative and radiographs when appropriate.
Diagnostic D0100-D0999
Report additional diagnostic and/or definitive procedures separately.
D0120 periodic oral evaluation – established patient
D0140 limited oral evaluation – problem focused
D0160 detailed and extensive oral evaluation – problem focused, by report
D0170 re-evaluation-limited, problem focused (Established patient; not post-operative visit)
D0171 re-evaluation – post-operative office visit
Diagnostic Imaging
The codes for image capture with interpretation are:
D0220 intraoral – periapical first radiographic image
D0230 intraoral – periapical each additional radiographic image
D0364 cone beam CT capture and interpretation with limited field of view – less than onewhole jaw
D0365 cone beam CT capture and interpretation with field of view of one full dental arch –mandible
D0366 cone beam CT capture and interpretation with field of view of one full dental arch –maxilla, with or without cranium
D0367 cone beam CT capture and interpretation with field of view of both jaws; with orwithout cranium
D0368 cone beam CT capture and interpretation for TMJ series including two or more exposures
Endodontic Retreatment
D3346 retreatment of previous root canal therapy – anterior
D3347 retreatment of previous root canal therapy – premolar
D3348 retreatment of previous root canal therapy – molar
D3351 apexification/recalcification – initial visit (apical closure/calcific repair of perforations, root resorption, etc.)
Includes opening tooth, preparation of canal spaces, first placement of medication and necessary radiographs. (This procedure may include first phase of complete root canal therapy.)
D3352 apexification/recalcification – interim medication replacement (apical closure/calcific repair of perforations, root resorption, pulp space, disinfection, etc.)
For visits in which the intra-canal medication is replaced with new medication. Includes any necessary radiographs.
D3353 apexification/recalcification – final visit (includes completed root canal therapy – apical closure/calcific repair of perforations, root resorption, etc.)
Includes removal of intra-canal medication and procedures necessary to place final root canal filling material including necessary radiographs. (This procedure includes last phase of complete root canal therapy.)
Pulpal Regeneration
D3355 pulpal regeneration – initial visit
Includes opening tooth, preparation of canal spaces, placement of medication.
D3356 pulpal regeneration – interim medication replacement
D3357 pulpal regeneration – completion of treatment
Does not include final restoration.
Unclassified Treatment
D9110 palliative (emergency) treatment of dental pain – minor procedure
This is typically reported on a “per visit” basis for emergency treatment of dental pain.
Anesthesia
D9210 local anesthesia not in conjunction with operative or surgical procedures
D9230 inhalation of nitrous oxide/analgesia, anxiolysis
D9248 non-intravenous conscious sedation
Professional Consultation
D9310 consultation – diagnostic service provided by dentist or physician other than requesting dentist or physician
D9311 consultation with a medical health care professional
D9430 office visit for observation (during regularly scheduled hours) – no other services performed
D9440 office visit – after regularly scheduled hours
Importance of Accurate Documentation
Keeping accurate and complete records, including images, x-rays, and any other relevant notes, is critical to reflect the quality of care delivered. The patient’s record needs to include sufficient information to justify the diagnosis and support the treatment plan and care ultimately rendered. Documentation matters for claims submission. Clear documentation will support the codes that you submit and also help reflect the entire course of treatment. This will also prove invaluable in case of claim rejections.
Simplify Root Canal Billing – Reach Out to a Dental Billing Expert
The Endodontists’ Guide to CDT © 2024 from the American Association of Endodontists provides various code scenarios to help dentists report root canals and other treatments. While successful root canal treatment process depends your careful attention, managing the billing and insurance aspects can be challenging. That’s where partnering with an experienced dental billing company can make the difference. Experts will handle the complexities of billing efficiently, freeing you up to focus on your patients.
Outsourcing endodontics billing can relieve your dental practice of the administrative burdens. From verifying patient coverage and benefits to submitting claims using the latest, accurate CDT codes, dental billing experts will ensure you receive the full reimbursement for the root canal treatments provided. An experienced dental billing company will work as an extension to your practice to optimize your revenue cycle management (RCM), prevent denied claims, and maintain a healthy cash flow.
Don’t let the complexities of dental billing distract you from patient care!