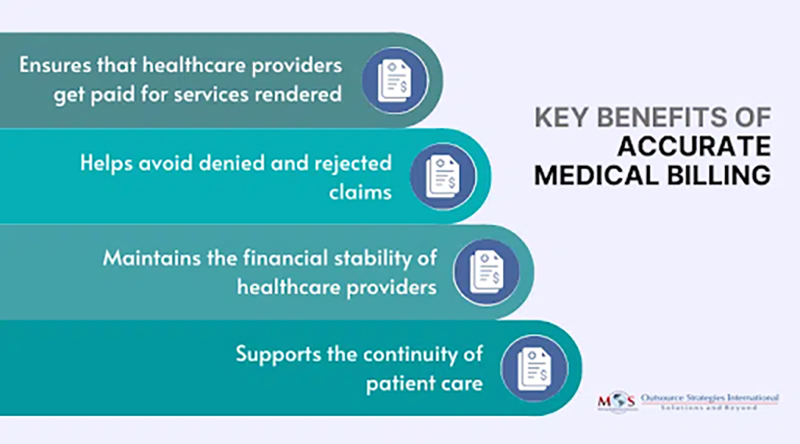
The medical billing process consists of certain well-defined steps to ensure smooth and efficient workflow and maximized financial performance. The steps range from patient registration to insurance verification to claims submission and follow-up payments. Even the slightest inefficiency or inaccuracy in any of the steps can lead to delayed payments, claim denials, increased costs, fines and penalties, and legal issues. Outsourcing medical billing is the answer when it comes to solving the various intricate issues and challenges faced by healthcare organizations.
This post will discuss the key steps to follow for a successful billing process and steady revenue. These are the strategies that experienced billers and coders providing medical billing services would follow:

How to Ensure an Effective Medical Billing System and Maximize Revenue
- Patient Data Collection
The first step is the collection of basic demographic information on a patient. Accurate and comprehensive data attained at this stage is the foundation for the subsequent medical billing processes. Your front-end staff is responsible for obtaining the following up-to-date information:
- Name
- Age
- Address
- Contact number
- Reason for visit
- Medical history
- Medical diagnoses
- Treatment plans
- Medication records
- Insurance payer name
- Policy number
- Allergies
Accurately collecting the above information is crucial for safe treatments of your patients, proper claim submission and overall efficient billing processing.
- Insurance Verification
Once registered, the next step is patient eligibility verification – verifying insurance information, benefits and coverage before the patient visit. This stage is crucial for determining what benefits a patient can receive from your proposed medical services. Insurance covers differ from one company to another and the information updated at any instance. So, regular verification is necessary to know if the services to be rendered during the visit are covered. In case a new visit involves costs to be met by the patient, they must be informed of it beforehand to avoid complications later on. You can verify insurance in these ways:
- Directly contacting the insurance companies on phone
- Checking online
Automating this work with specialized software can lessen the labor of manual work, reduce human error and claim denials, and ultimately obtain timely reimbursement for your service.
- Create Super Bills
Once the patient leaves the facility, the summarization of all the updated information, medical reports, and services given to the patient from the visit into one single document is called the super bill. It is a comprehensive list containing vital information that is needed for payers to reimburse the services rendered. Any missing information or slight error may lead to claim denial.
The following information should be validated:
- Provider and clinical information
- Patient contact information
- Patient’s demographic
- Patient’s medical history
- Procedures and services information
- CPT and ICD-10 codes
- Dates of service
- Applicable diagnosis
- Each service amount and total cost
- Accurate Coding:
Every procedure, diagnosis, and service provided to the patient should be accurately and promptly translated into specific, standardized codes using medical coding systems such as:
- Current Procedural Terminology (CPT)
- International Classification of Diseases, 10th edition (ICD-10)
- Healthcare Common Procedure Coding System (HCPCS)
- Diagnosis-Related Group (DRG)
- National Drug Code (NDC)
Maintaining accuracy in medical coding is crucial for receiving adequate payments from insurance providers. Using the wrong codes could lead to claim denials, delayed reimbursements and claim resubmissions. That’s why it’s important for you to employ certified medical coders who are well-versed in the latest coding practices, as the insurance providers frequently change the coding regulations.
- Charge Capture:
Charge capture is meticulous documentation that involves recording every service delivered and inputting the entire healthcare costs into the billing program. Medical billers track all the medical data and their corresponding medical codes with the appropriate amount for your services. This bill is used to create claims.
If you haven’t already, consider employing Electronic Health Records (EHR) systems in your practice for accurate data entry that will help minimize the risk of errors.
- Claim Submission:
Once the claim is compiled and checked for accuracy and compliance, it’s time to file it. It is submitted via Electronic Data Transfer (EDI) and must pass through two steps:
- Scrubbing – All the relevant data in your claim form is verified by Electronic Health Record (EHR) software. It checks for specific coding-related errors and any incomplete field left on the form.
- Clearing House – A third-party organization that acts as a liaison between your practice and insurers. This company is in charge of checking patient records including current insurance date, name, date of birth and any other potential coding issues, and send them to health plan companies.
Despite following all the steps in the medical billing workflow precisely, claim rejection is a situation that you will likely have to face occasionally. In that case, you may need to resubmit the claim after re-checking all the information provided.
- Claim Adjudication:
After you’ve filed a claim for payment, the insurance payer evaluates if it is valid or not. Your claim could be accepted, rejected or denied. Here’s what to do in each case scenario:
- Claim accepted – This is when your claim is accepted without any coding or data entry errors and they approve it. After approval, you will receive an explanation of benefits (EOB) statement. EOB statements contain details such as check details, claim number, service description, amount your practice charged, and the amount payers covered and did not cover.
- Claim rejected- If your claim’s essential data is missing in the application or if there’s a coding mistake, it’ll be rejected and sent back to you. In such a situation, you must make the necessary changes and resubmit the claim.
- Claim denied – Your claim could be denied for a number of reasons, ranging from the procedure performed missing in the form to your practice being out-of-network. A denied claim means delayed or lost revenue. If this happens you have the option to file for an appeal either to the insurance company or your state’s insurance regulators.
- Patient Statement Preparation:
Prepare a patient statement highlighting the following information:
- A complete account of procedures and services rendered to the patient
- The costs of the given services
- The amount covered by the patient’s payer
- The amount to be paid by the patient
You can also attach an explanation of benefits statement issued by the insurance provider to elaborate the services covered and not covered by their healthcare plan, so the patient understands why they owe you money despite having insurance.
- Payment Posting::
Payment posting is the process of recording payments received from insurance companies and patients into a medical practice’s billing system. Though it may seem like a back-end task, accurate and timely payment posting is critical to maintaining healthy cash flow and identifying revenue opportunities.
When done correctly, payment posting ensures accurate financial records, speeds up the revenue cycle, reveals payer trends and issues, supports compliance, and helps identify mismatches between expected and actual payments.
- Follow up:
The final step involves issuing and mailing out the bills on time to the patient. Ensure that the clients pay the bills within the assigned deadlines, and the failure to do so on their part can initiate a follow-up protocol. You can either approach the patient directly or hire a collection agency.
Optimize Patient Payments with the Right Strategies
It is crucial for health care practices and organizations to also take proactive steps to optimize patient payments. Here are some good strategies to adopt.
- Provide a choice of payment options: Make it easier for patients to pay by offering them a wide variety of options such as point of service, phone, web, credit card, debit card, and check.
- Payment any time: Implement an online bill payment option that will enable patients to pay any time, at their convenience.
- Payment in installments: Accept payment in installments from patients in financial difficulty, but have a well-defined payment plan to ensure compliance.
- Communicate: Have materials and strategies in place to communicate the practice’s payment policy.
- Educate patients: Train staff to communicate and be transparent with patients about their costs, options and financial responsibilities as stated in their insurance contract.
- Automated reminders: Send out automated reminders to patients that co-pays and previous balances are due at the time of service.
Medical billers and coders in your practice should have excellent knowledge of Local Coverage Determinations (LCDs.) This will help to clearly understand the circumstances under which the procedures are covered, as well as get details about coding guidelines and reimbursement. Another important consideration is verifying the denials. Sometimes the claim may be made correctly but the insurance companies or the billers can make a mistake and this may lead to claim denial. Medical billing staff should also be proactive about appealing denials. This is because payers do not always follow the proper guidelines. You can often have a claim settled by providing documentation as to why that claim deserves reimbursement. Checking your electronic submission reports helps ensure whether claims are submitted and received by payers. The reports also show the rejected claims. With the help of these reports you can find the mistake and again resubmit the claim for a speedy approval. Claims that didn’t reach the payer can also be investigated and errors corrected. Know the exact amount the payer should reimburse and calculate the exact payments to prevent loss of money. The billers should register all details of the patient in the payer’s website. Also, billers should refresh their knowledge regarding the changes and updates occurring in the medical billing industry.
Wrapping up, medical billing is a key catalyst that directly impacts the financial growth of your practice. Outsourcing medical billing isn’t just an option, but a necessity to keep up with the challenges of today’s healthcare system. Outsourcing can ensure implementation of coding and billing best practices to reduce claim denials and improve your revenue cycle. There are many outsourcing companies offering a free trial option for their services. This will help evaluate the service quality and turnaround time.